Last updated on
Want to make use of solar energy to create a warm environment for plants or your pleasure? Here are the ideas for the ultimate solar greenhouse. Read on!
You might now it as simply a greenhouse, but it’s referred to as solar greenhouse because it traps solar energy. Anyone can build it too. Your success will depend on how much sunlight you get in your location. If the answer is “not much”, don’t let that discourage you – there are solutions for every climate zone. We’ll go over that in a bit.
Why would you want a solar greenhouse anyway?
- Growing plants is an obvious one (for your use or to sell.)
- But you can also create a warm environment to spend time in during the cold season.
- Hang a hammock!
- Create a place for a hot tub all year round.
How Does a Solar Greenhouse Work?
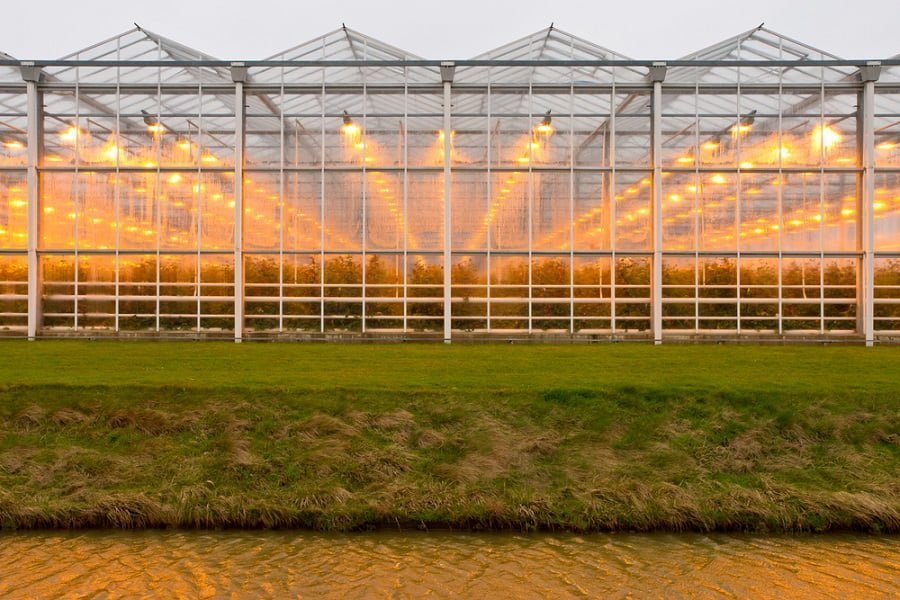

A solar greenhouse uses sunlight instead of fossil fuels to create a warm environment for plants. Heated floors warm the air above, causing this to rise while colder air falls. The convection current heats the entire greenhouse, enabling the growth of exotic plants in colder climates all year round.
How to Make a Greenhouse?
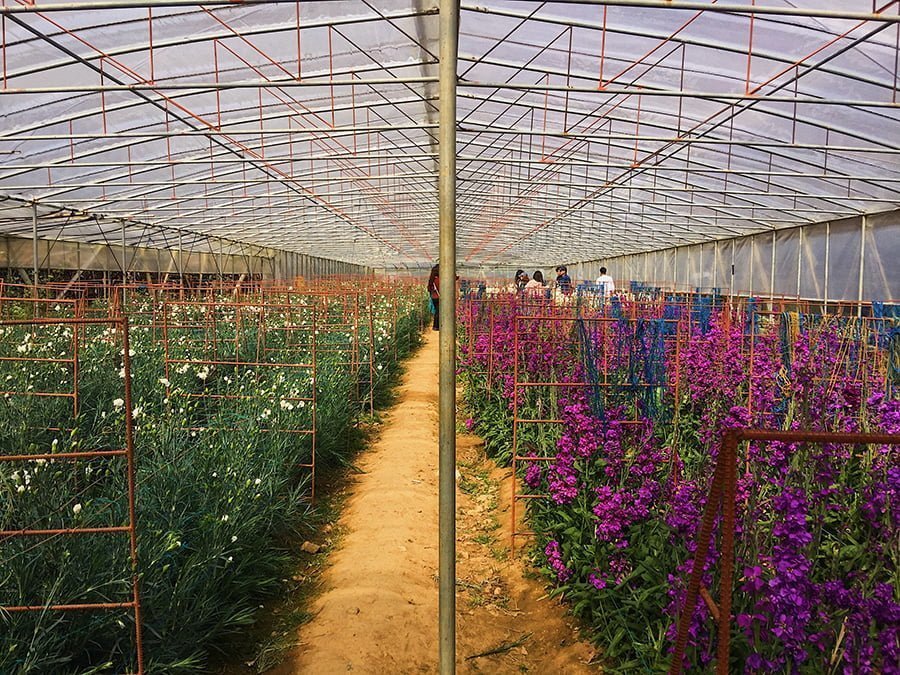

Start by orienting the greenhouse towards the sun. The biggest windows should face the south and the west to maximize sunlight if you are in the Northern hemisphere. The rest of the walls and the ground should be insulated to trap the heat. Maximize natural ventilation to prevent pathogens, molds, and insects.
Passive Solar Greenhouse
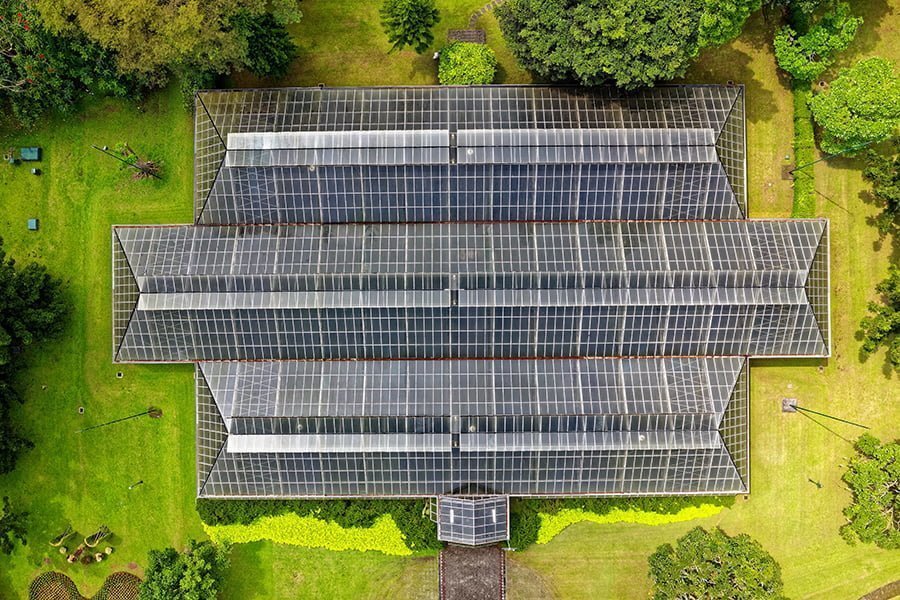

While all greenhouses use the sun’s energy, many of them rely on fossil fuels to provide additional heat. A passive solar greenhouse, on the other hand, goes all-natural by relying solely upon the sun.
It also uses concrete or other forms of thermal mass to store heat. The result is a more economical and eco-friendly structure.
Greenhouse Plans
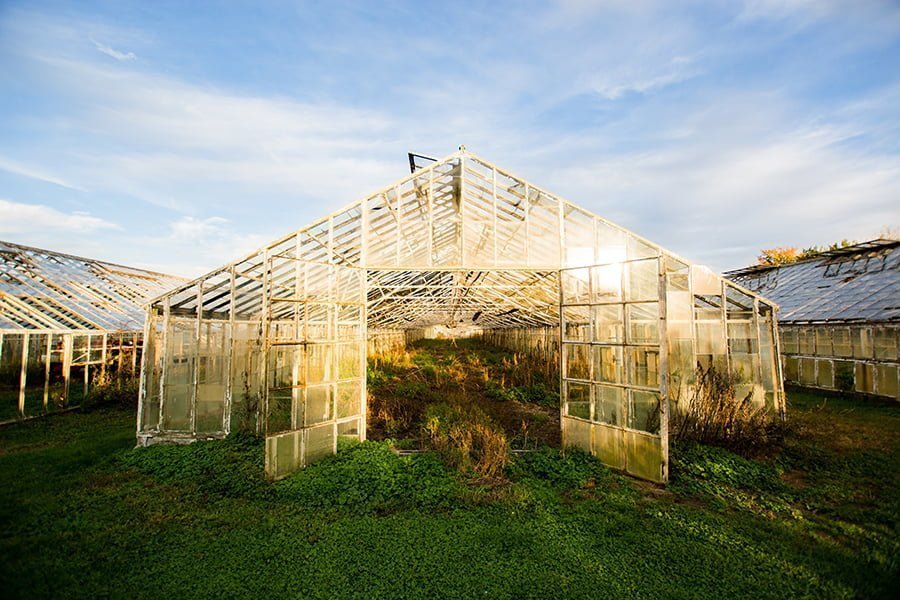

Greenhouse plans can go from simple to complex. It’s good to check existing ones that closely reflect what you have in mind.
Most are nothing more than bare timber frames with glass or plastic sheets on all sides. Others, like a geodesic dome greenhouse, are more strategic with the sun-facing borders, the overall shape, and the extra features.
Greenhouse Design

Greenhouse design must consider all the factors that can affect the health of the plants within. Everything must revolve around the purpose of the structure which could be cloning, hydroponics, propagation, and so on.
Special attention must be given to insulation, ventilation, orientation, heat retention, efficiency, solar lighting, structural integrity, and budget.
Greenhouse Materials
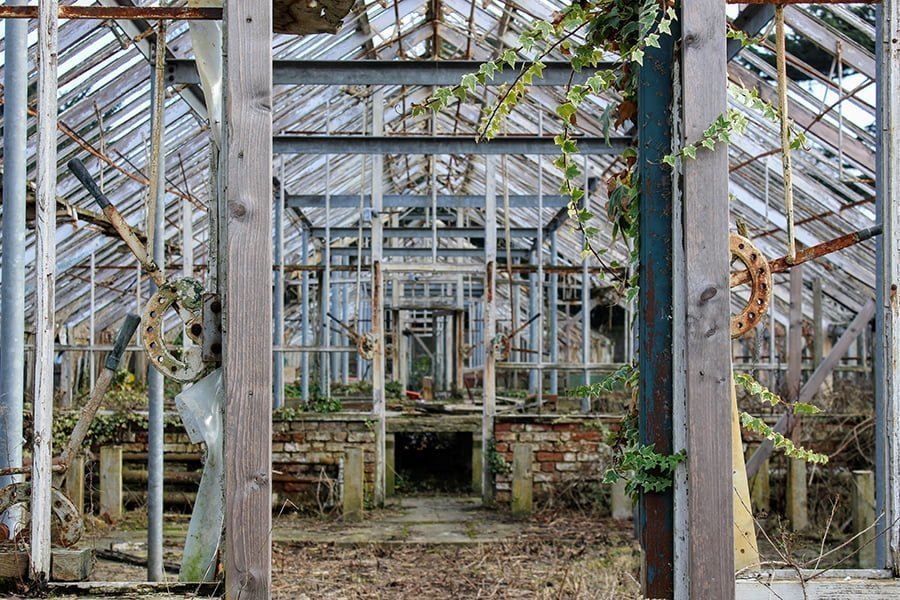

Greenhouses need to be light, strong, economical, efficient, and adaptable. Given these requirements, the common materials used in construction tend to be:
- Wood
- Iron
- Steel
- Aluminum for the pillars, arches, and supports.
Meanwhile, concrete is used for the foundation. Glass, plastic films, and polycarbonate are used for the covers.
In-Ground Greenhouse

This type of greenhouse is built for extreme energy efficiency. You dig a hole in the ground of about 4ft to 8ft to guarantee constant temperature year-round. It is around 10 degrees warmer in-ground than above ground. This ensures a steady ideal environment for plants to grow even in winter.
Year-Round Greenhouse
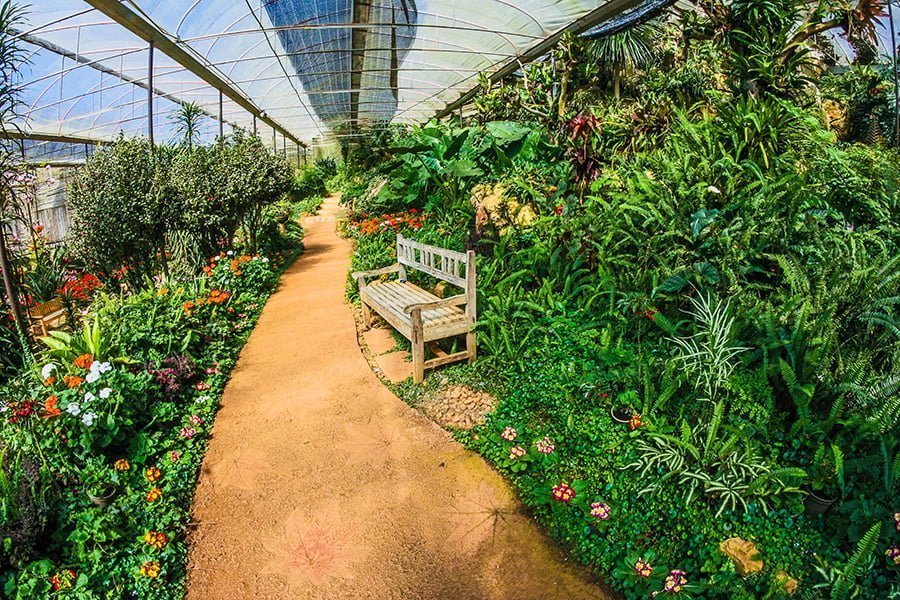

To make a greenhouse functional year-round, you need to optimize heat absorption and storage. Use materials with high thermal values such as water in black barrels to store heat. Get glazing that holds more heat based on R-Value such as thick fiberglass. Utilize the power of the sun for efficient heating.
Chinese Greenhouse
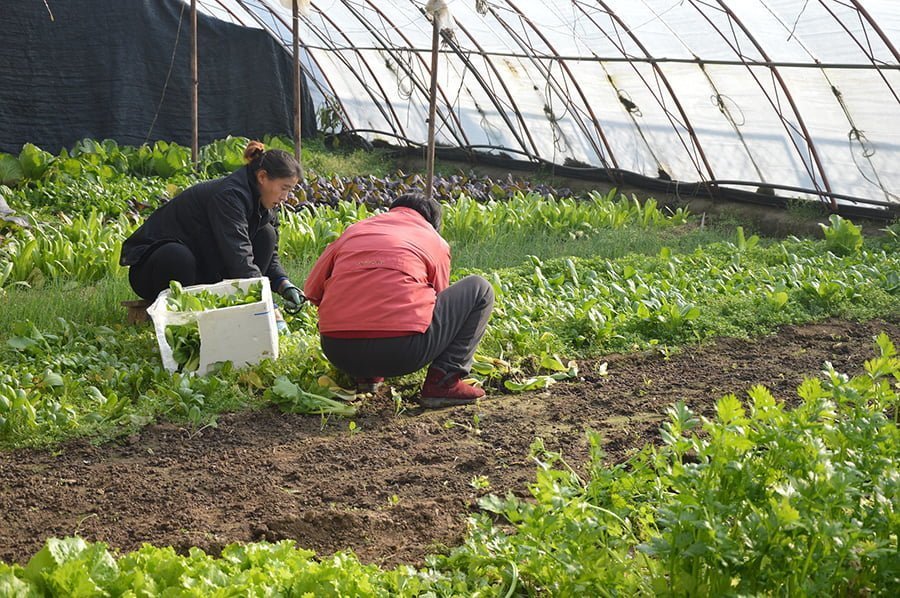

Eastern cultures have developed ways to keep growing plants in the winter for millennia. The Chinese have been particularly successful thanks to agricultural traditions and government incentives in the past few decades. Most of the modern ones use transparent plastic film and synthetic insulation blanket. Some use double roofing or reflective insulation.
Industrial Greenhouse
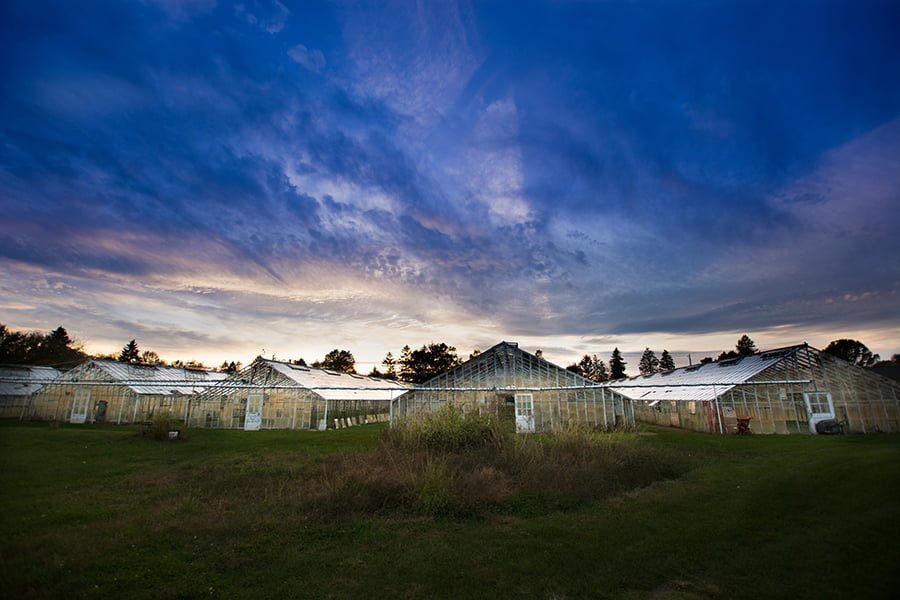

Large companies build industrial greenhouses to keep growing plants for mass consumption. Given the high stakes, these require excellent reliability and energy efficiency while keeping the costs low. Their size can rival office buildings and their temperature control systems boast extreme precision.
Modern Greenhouse
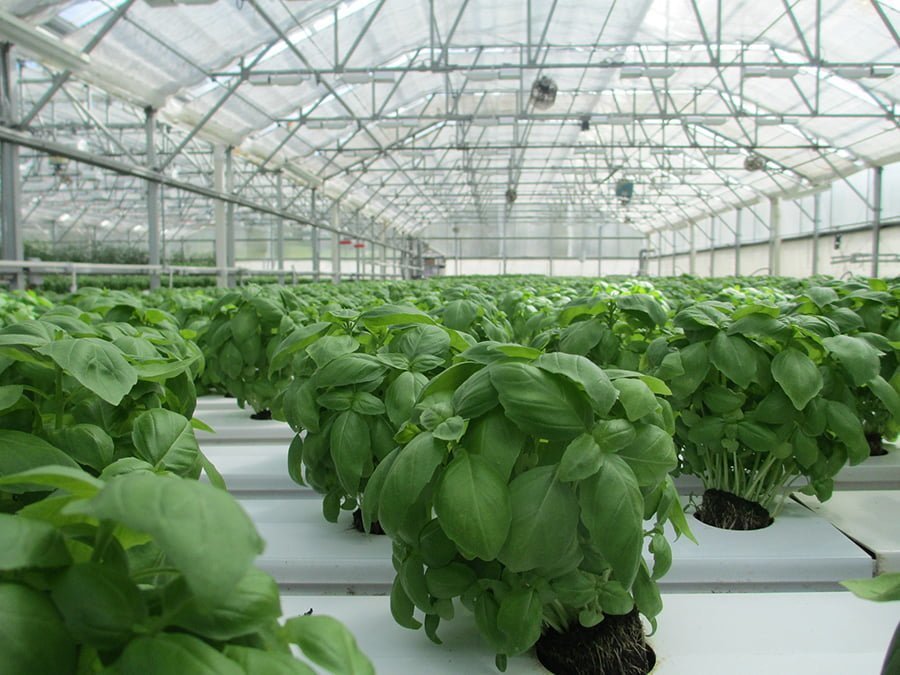

The modernity of newer greenhouses manifests in different ways. Some may borrow design aesthetics from modern architecture with clean lines, a reliance on metals, and neutral colors. Others will take it a notch higher with impressive technologies such as automatic temperature control and computer-based pest monitoring systems.
Small Greenhouses
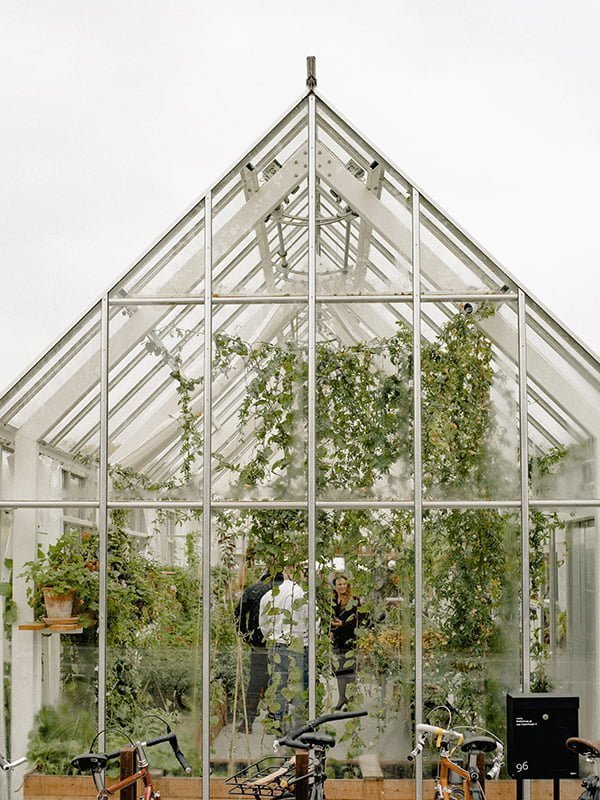

Small greenhouses can be constructed in modest backyards to promote sustainability and productivity. The smallest ones are just 2ft by 4ft by 2ft which makes them viable even for condos and apartments. Others are virtually tall metal shelves with plastic covers to hold a few pots. There are also walk-in greenhouses that are 6ft on all sides.
Glass Greenhouses
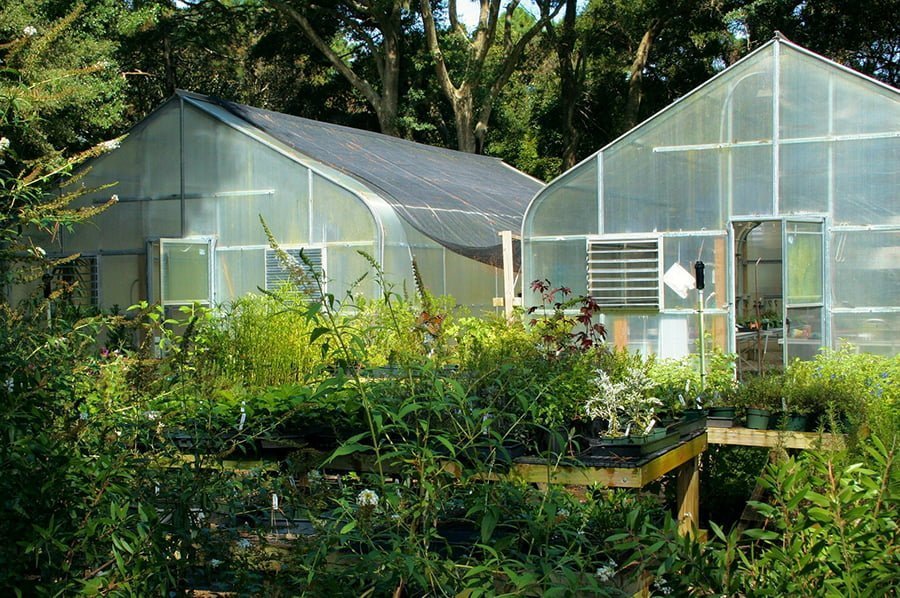

People opt for glass greenhouses over plastics primarily because of clarity and transmission. Glass panels allow more light in comparison to polycarbonate and it won’t fade over time. This means a higher potential for photosynthesis, as well as greater heat absorption. Glass is inert, long-lasting, UV resistant, non-combustible, and easy to maintain.
Greenhouse Insulation
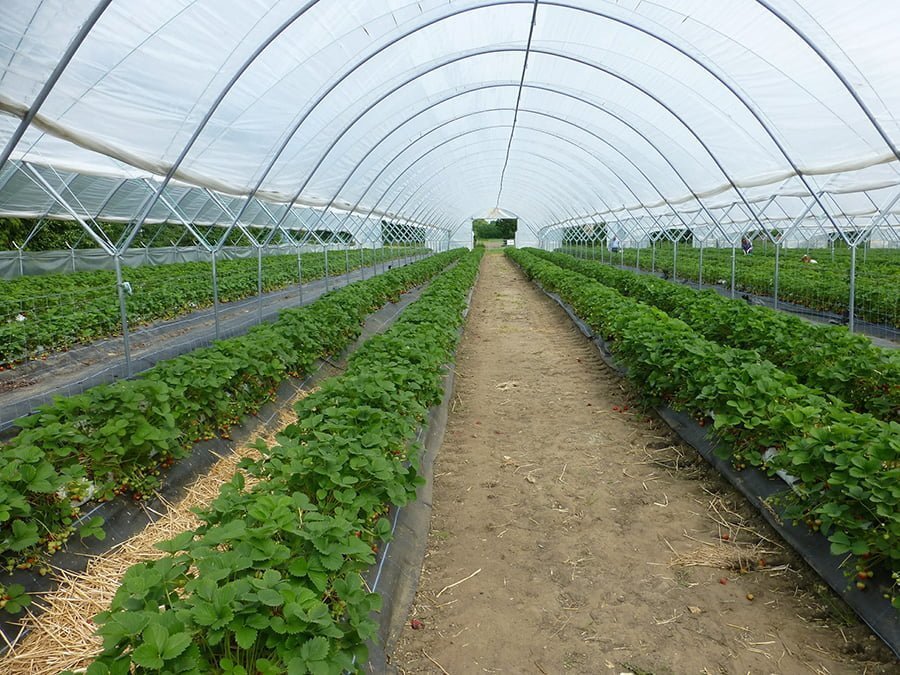

Insulation is necessary to prevent heat from escaping and keep the plants warm. Gaps must be sealed and insulating material must be spread across the walls. Bubble wrap is a cheap and easy way to do this. Old blankets and thermal insulation foil may also be laid out at night. Polystyrene can double as a seedling tray. If you have more funds, then go for thick polycarbonate panels.
How to Heat a Greenhouse?

Greenhouses are primarily dependent on the sun for heating using a heat sink (barrels of water can work great for this). As long as the exposed areas are large enough and positioned the right away, then daytime warmth should not be a problem. Some people also rely on electric heating and use fans to circulate the warm air.
Solar Greenhouse Heater

To heat up greenhouses, you can store solar energy in a thermal mass (heat sinks) such as concrete or water. Stack barrels in direct sunlight and place the more delicate plants near them. You can also use a heat exchanger or a powered heater using solar panels.
Solar Powered Greenhouse Fan
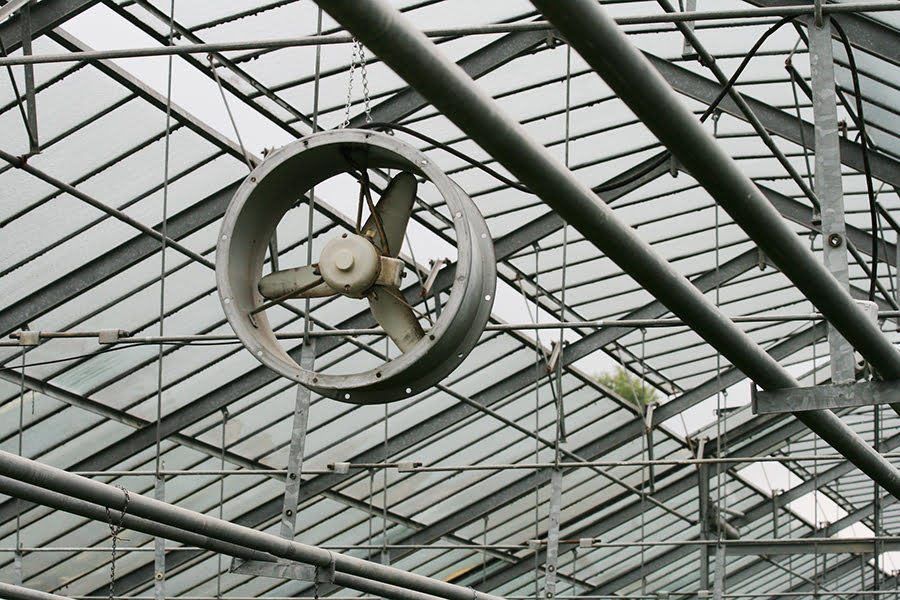

Ventilation is crucial in warm areas. Inside a large greenhouse, you can use solar-powered fans to improve circulation. Use low-power motors and attach these to solar panels for high efficiency and low operating cost.
Greenhouse Siding
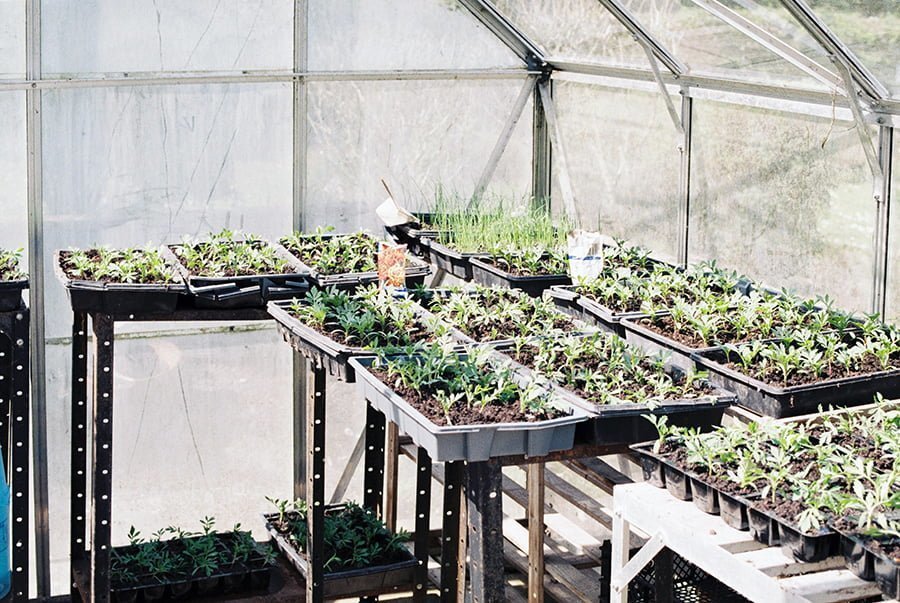

Glass is the best siding when you consider light transmission, clarity, UV resistance, and aesthetics. However, plastic is more commonly used thanks to low cost, multiple options, lighter weight, and better durability. You can use thin plastic film, rigid polycarbonate panels, flexible fiberglass, and many more.
DIY Lean-to Greenhouse
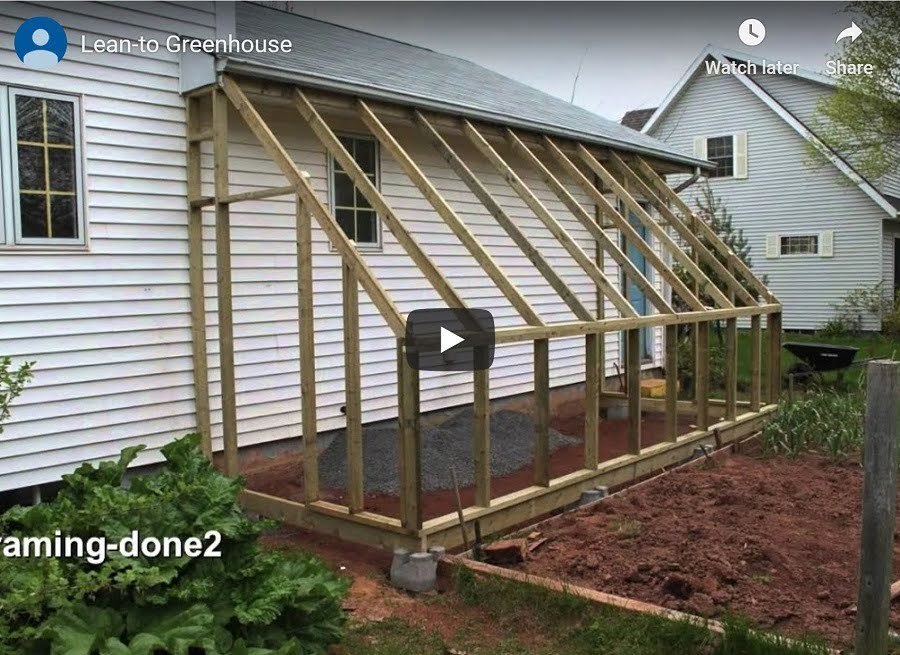

A lean-to greenhouse is built against an outside wall of the house to reduce cost, ensure durability, save space, increase heat retention, and improve monitoring. DIY enthusiasts will find them easier to build than standalone designs. A successful project will also increase the property’s value.
Table of Contents