Last updated on
So you’ve decided to grow bamboo. Now what? Here’s all you need to know about growing bamboo of all types, whether you’re doing it for sustainability or Feng Shui.
You may have heard about the Chinese Bamboo Tree. It provides a unique lesson in patience in all things in life. It goes saying that it takes extraordinary patience to grow a bamboo Tree.
You plant the seed and water it regularly. Nothing happens during the first year. You must continue watering the tree for years two, three and four, but there is no reward for your work. In the fifth year, however, the most amazing thing happens. The tree grows up to 90 feet within a week.
This may be a hyperbole, however, it says a lot about growing actual bamboo. In real life, it depends on the type of the plant. Some types of it are very easy to grow, others take careful planning and care.
Our goal in this post is to clarify everything about growing your own bamboo.
How to Choose the Right Type of Bamboo Plant

As there are several types of the bamboo plant, and they are quite different, you need to choose right before deciding what to grow. Your choice will depend on what you want to get from growing it in the first place.
So here’s how you can decide:
- For decorative value and Feng Shui (i.e. growing it indoors) choose Lucky bamboo. It’s easy to grow and you can use simple containers for it. It can be as easy as growing a single stem.
- For timber, choose the giant timber bamboo. You’re looking at a small plantation of your own in this case. So be prepared to put in some effort to grow it properly in your garden. You may sell this timber or use it in crafts.
- For outdoor privacy screens, choose running bamboo. It propagates and grows quickly. However, you will need to take measures to control its growth.
- For most other cases outdoors, clamping bamboo will make a relatively easy-to-care-for plant.
- For cooler climates, you will have to choose cold hardy bamboo.
Types of Bamboo
There are many different types of bamboo that can be used in various applications for interior design, gardens, patios, and decks. Knowing how to grow bamboo depends specifically on the type. Some of the major types that might prove useful in your garden include:
- Clumping Bamboo: This type of bamboo spreads in a U-shape, instead of horizontally.
- Fargesia Bamboo: Fargesia bamboo belongs to the class of flowering plants and is often used as ornamental plants.
- Guadua Bamboo: This Neotropical variety is thorny and grows in clumps. A moderate to large species, Guadua bamboo is eaten by many kinds of wildlife as a dietary staple.
- Lucky Bamboo: This variety of bamboo is the perfect choice for growing indoors.
- Chilean Bamboo: This bamboo is a good choice for gardeners who want to learn how to grow bamboo because it’s frost-tolerant and widely grown in temperate regions all over the world.
- Runner Bamboo: Grown in almost all climates, Runner bamboo propagates aggressively because it uses both monopodial and leptomorph growth.
- Arrow Bamboo: Arrow bamboo produces the stiff canes that Japanese Samurai wield in battle, but the bamboo grows freely in temperate zones in the United States from Florida to Connecticut.
- Dwarf Green Stripe Bamboo: This variety of bamboo is native to China and Japan, but it grows in climates as cold as Minnesota. The plant grows vigorously through underground rhizome propagation, and it can become invasive.
- Black Bamboo: This plant, which is native to Indochina and the Himalayas, also spreads aggressively through underground rhizomes. The wood is often used in high-end sustainable furniture.
- River Cane Bamboo: This native American plant, common in the southern and southeastern parts of the country, is a good choice for U.S. gardeners.
We’ll go over the most popular bamboo types to see how growing each of them is different.
Lucky Bamboo
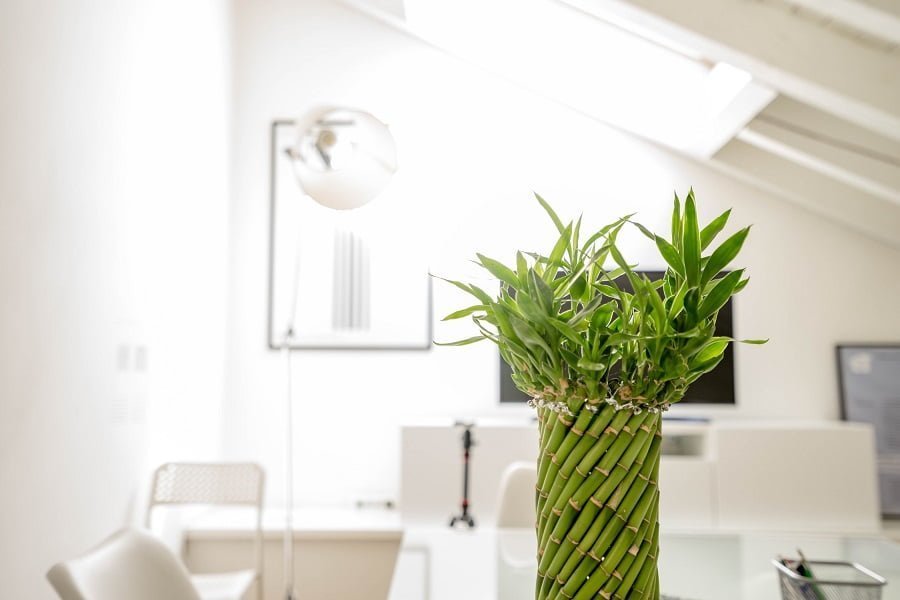

Lucky bamboo grows well as a houseplant, and the plants are used in Chinese culture for feng shui. Different numbers of stalks have different meanings in Chinese culture, but the hardy plant is generally considered good luck.
How to Grow Lucky Bamboo
Here are the key things you need to remember:
- You should water Lucky bamboo sparingly and keep it out of direct sunlight.
- Arrange your stalks for better feng shui.
- Remove dead or yellowed leaves.
- Tie the stalks with ribbon or wire to grow in unique shapes.
Clumping Bamboo

Clumping bamboo grows in U-shaped areas, and you don’t need to worry about the plant spreading beyond its territory in your garden. The plant only spreads about 2-3 inches per year. The bamboo grows between 8 feet and 25 feet tall.
Running Bamboo
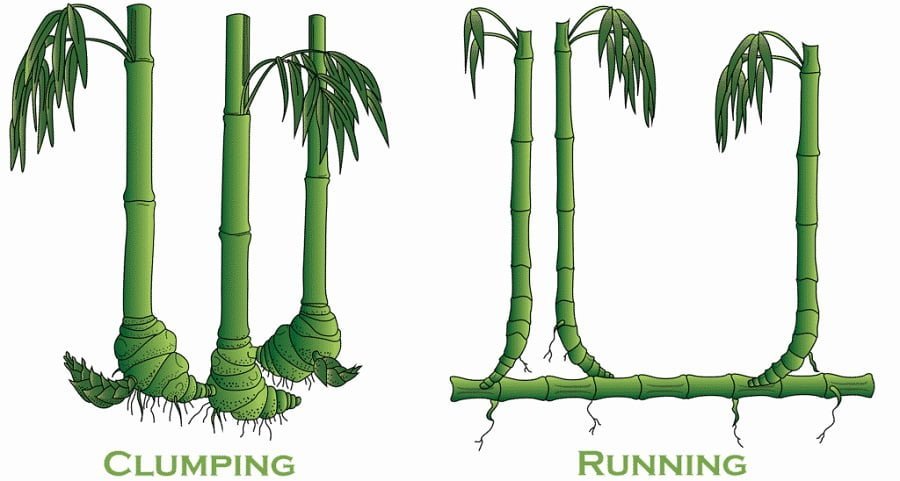
Running bamboo is also one of the most popular kinds of bamboo for home gardens, but unlike Clumping bamboo, it can be invasive. However, there are ways to prevent the bamboo from taking over your garden.
How to Grow Running Bamboo
Here’s what you can do to manage the growth of this type of bamboo plant:
- Erect a plastic barrier that extends 30 inches into the ground.
- Use a shield which will enable you to grow running bamboo as a natural privacy fence.
Cold Hardy Bamboo
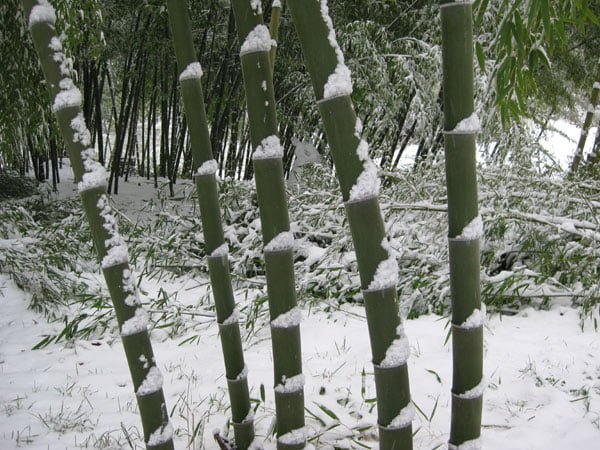

Cold hardy bamboos enable home gardeners to grow tropical bamboos in climates that reach lows of -10°F. You can add a splash of tropical vegetation in most U.S. regions.
Timber Bamboo
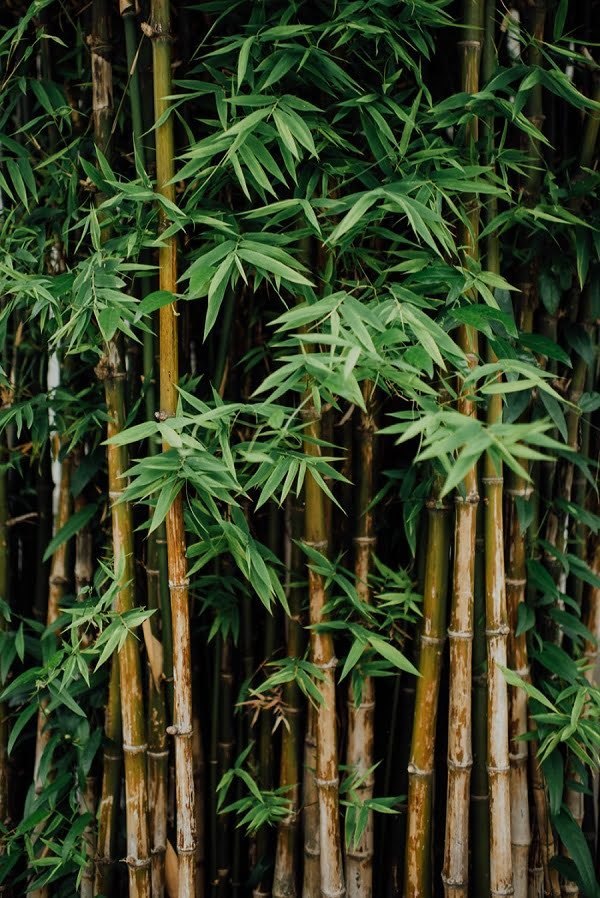

This hearty species rank among the largest of bamboos that grow in temperate regions. The bamboo grows up to 40-feet and 6 inches in diameter. Being the most common type of bamboo plant it’s best suited for use in furniture making (although not construction).
How Fast Does Bamboo Grow?
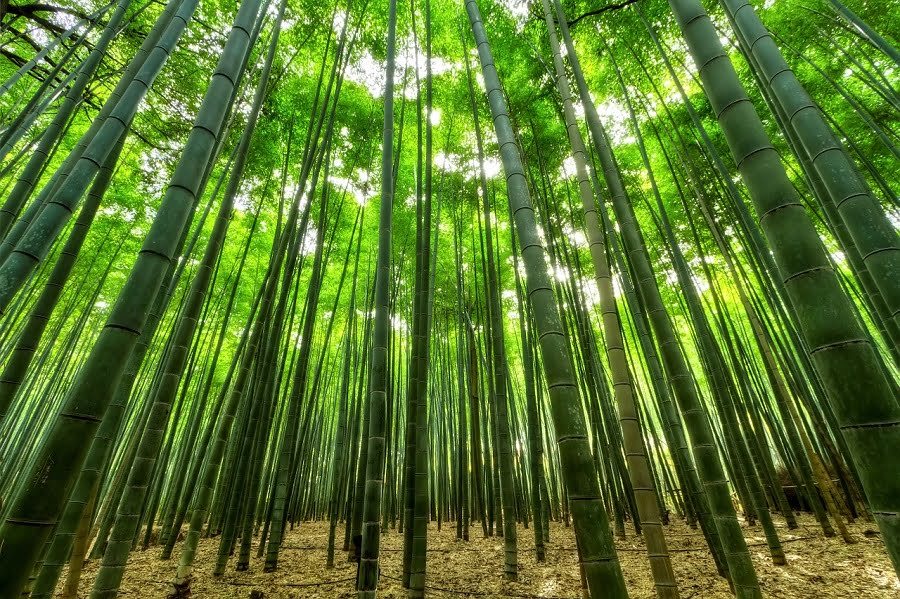

Bamboo grows so fast that it is the world’s most sustainable source of wood. The plant’s unique rhizome characteristics also ensure the fastest propagation of most species.
A planted bamboo tree takes 3-4 years to grow to its full height.
Some species grow up to 36 inches within 24 hours – about 1 millimeter per second.
Fastest Growing Bamboo
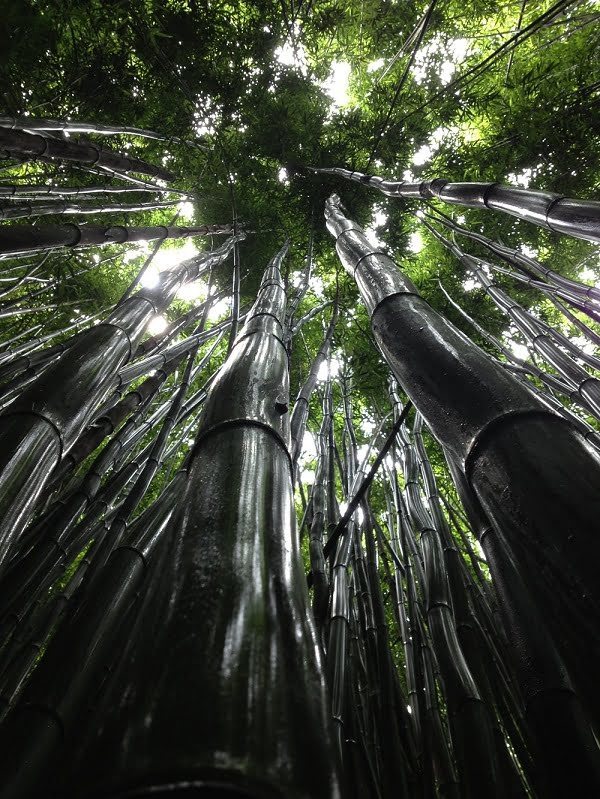

There are several species of bamboo that can grow up to 36 inches a day. These include Giant timber bamboo, Chinese Moso bamboo, Madake bamboo and other members of the Bambusa and Phyllostachys genera.
Growing Bamboo Indoors
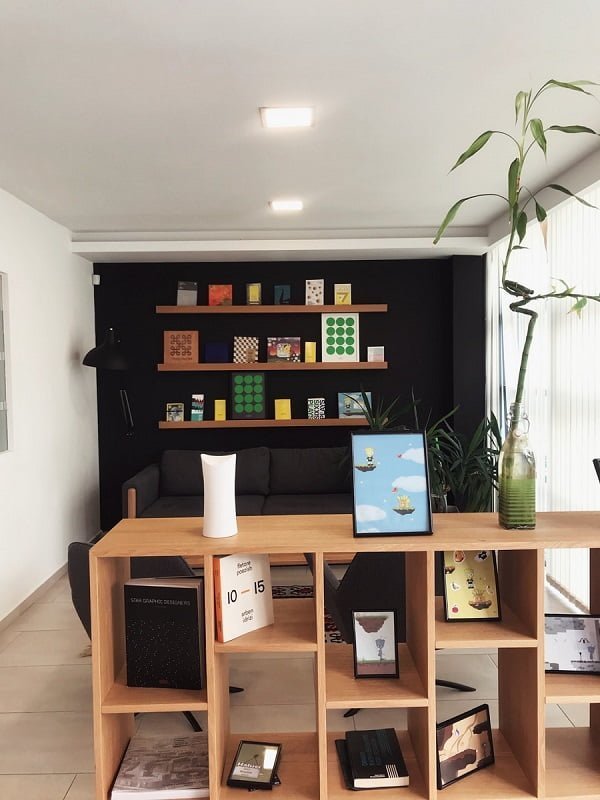

You can grow bamboo indoors. Choose a wide pot that’s twice the diameter of the root ball. Plant the bamboo at a shallow depth, and fill the pot with soil that drains well. The most common and easiest to grow indoors is Lucky bamboo.
The purpose of growing the plant indoors is either decorative or energetic (if you follow Feng Shui). In some cases growing it indoors can be as simple as growing a single stem in a jar filled with water.
All of the same bamboo care rules apply to indoors:
- Water it weekly
- Avoid direct sunlight but provide plenty of it
- Use containers that are big enough to grow
- Cut the stems to shape the plant
Potted Bamboo
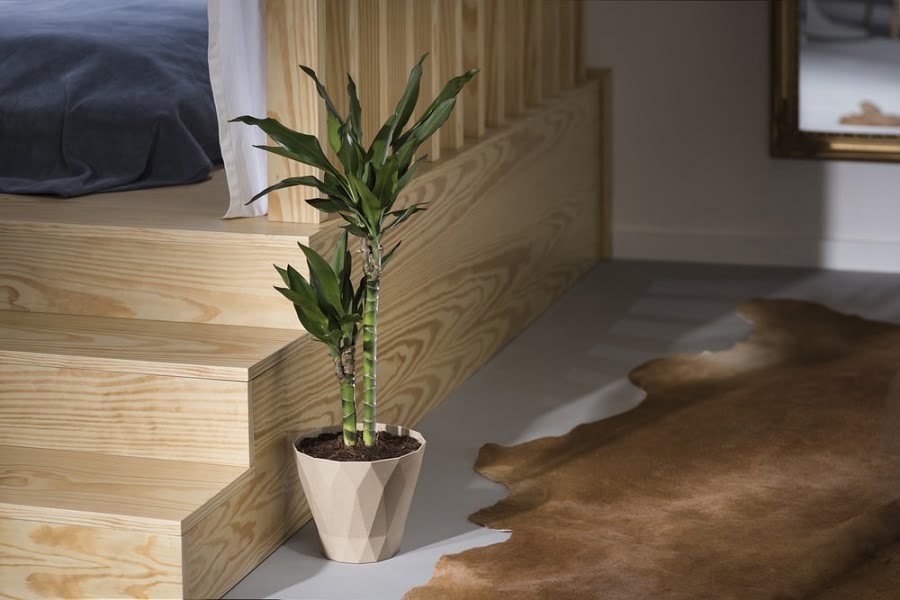

Most types of bamboo can be grown in containers, and you can even grow a natural privacy screen. Maintenance can be more involved than caring for common houseplants. Bamboo can quickly outgrow the pot and become root-bound.
Bamboo Planters
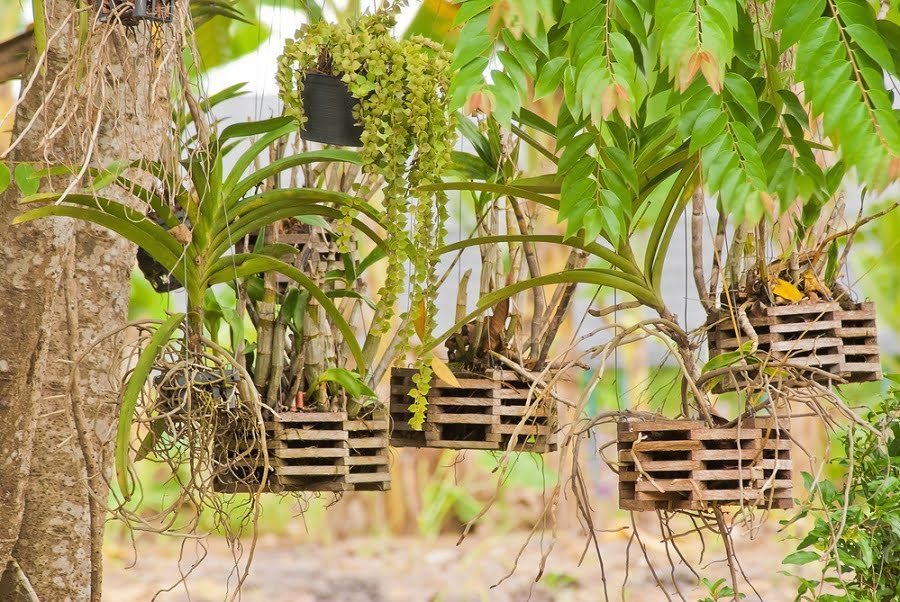

Bamboo planter boxes can enable you to build a privacy screen, highlight your patio or decorate your garden. Planter boxes should be at least 18″ X 18″ and 18″ deep.
If you want a taller privacy barrier, 36″ tall outdoor planters are available. They come in a variety of colors and materials such as powder-coated steel or resin. Planter boxes can also be used to create displays or separate areas within your garden.
Planting Bamboo
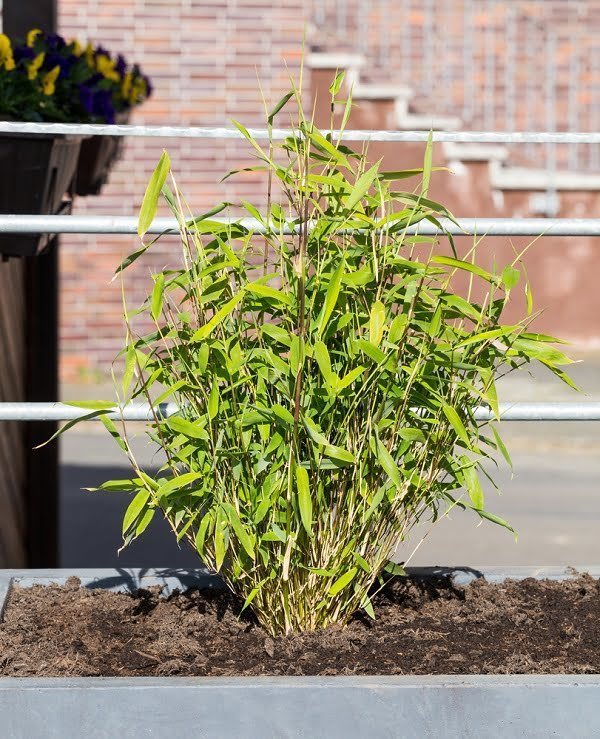

Planting bamboo is relatively easy, and the two most common garden types – Clumping and Running – require radically different strategies.
Clumping bamboo grows slowly in a predefined U-shape, but Running bamboo propagates aggressively in all directions.
You can put up barrier shields to keep Running bamboo from taking over your garden. The best time to plant bamboo is in the early spring, but well-rooted plants can be planted in summer.
How to Propagate Bamboo
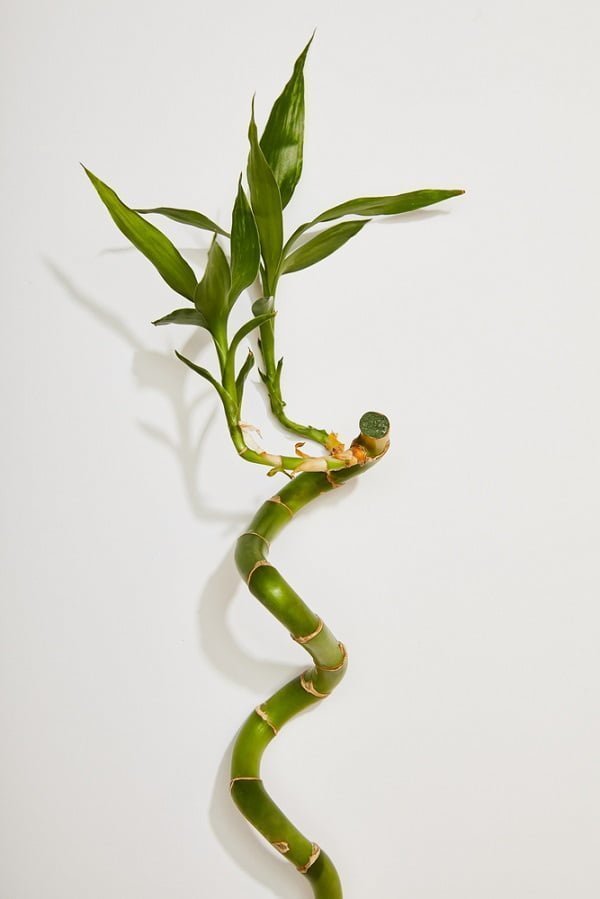

You can grow new bamboo plants from rhizomes, cuttings, offsets, and seeds, but most species flower and seed rarely.
Here’s how:
- Cut off a rhizome with 2-3 growth buds.
- Plant it in a pot.
- Cover it 3 inches of soil and water it
- Cut sections of the bamboo stalk with 3-4 growth rings
- Put them in water to generate roots.
- You should cut the end to be placed in water at an angle to increase the surface area for better absorption.
How to Take Care of Bamboo
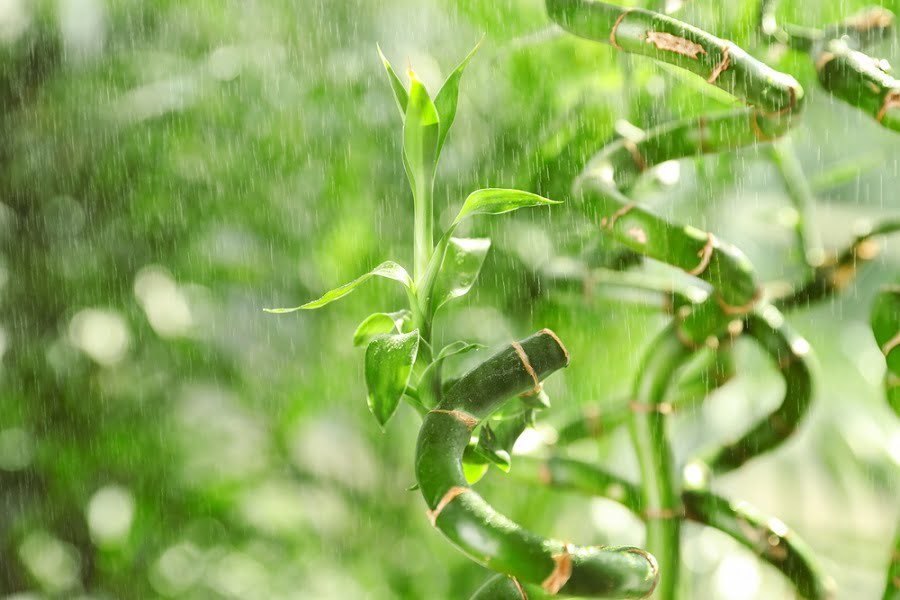

Bamboo needs about 1 inch of water a week – from rain, irrigation or manual watering. Watering the plants will help them develop deeper roots, which protects them during drought conditions.
Bamboo is versatile and hardy, but the plants will grow faster in full sunlight.
Fertile and slightly acidic soil is best, and the soil should drain well.
How to Transplant Bamboo

Some bamboo plants only flower once every 50 years, so transplanting bamboo might be necessary. Here’s how:
- Take a part of a bamboo clump by digging up a root clump.
- The roots are very sensitive to the sun and dry conditions, so you should immediately place the clump in a bucket of water.
- You should have a hole dug and ready for the transplanted bamboo.
Roots and Rhizomes
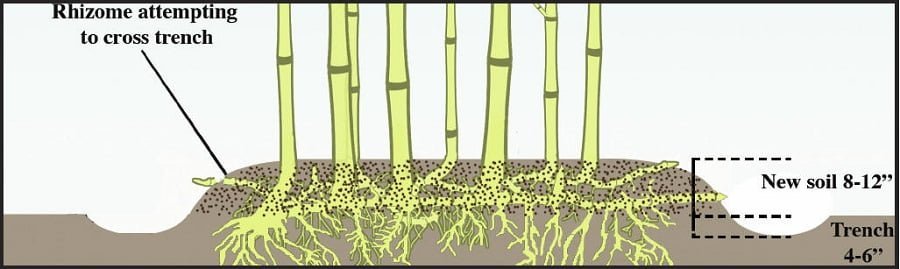
Bamboo roots and rhizomes are the traditional way that the plants grow and spread. An offset is a section of root that splinters off the root system and grows a separate plant. Rhizomes are traditional buds that many kinds of vegetation use to propagate – especially grasses.
Bamboo Leaves

Bamboo leaves range from medium to large-sized, and they contain lots of silica that bamboo plants need. That’s why it’s best not to rake up dead leaves – they self-fertilize your bamboo plants, and they decompose within a year, so you won’t experience a backup of leaves.
Bamboo Turning Yellow
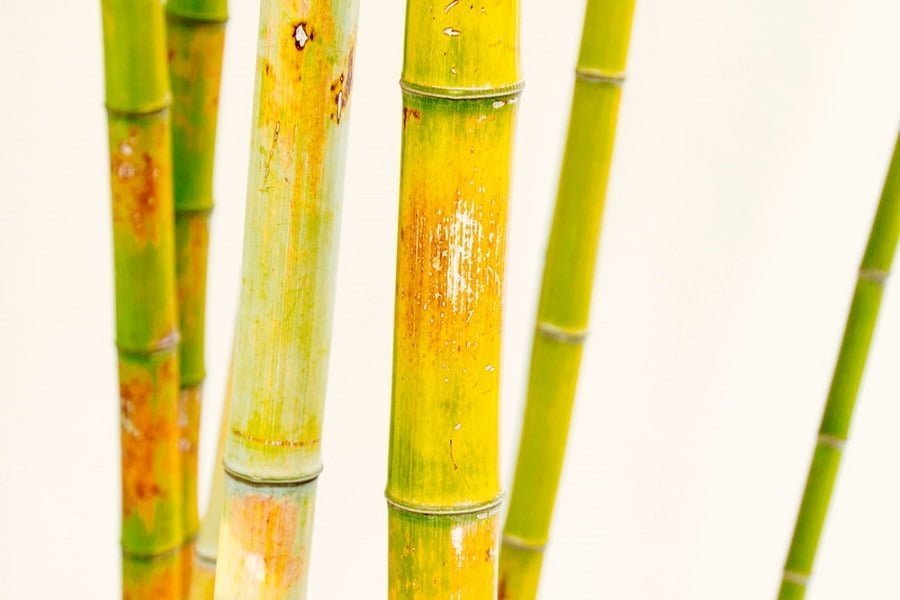

The most common causes of bamboo turning yellow include too much sun and salty or chlorinated water.
Bamboo Fertilizer

Bamboo grows better with organic compost, and bamboo leaves provide a natural fertilizer. You can use organic fertilizer to top-dress the planted area. Watering is necessary to distribute the nutrients to the roots.
Bamboo Uses

Bamboo is one of the most versatile crops in the world. Bamboo can be used for landscaping and decor, building roads and pathways, medicinal purposes, food for people and animals, furniture, clothing, bamboo sheets, accessories, and building homes.
Growing Bamboo for Profit

You can grow bamboo plants and sell them for thousands of dollars using a backyard nursery. Landscapers and homeowners pay between $30 and $150 for potted bamboo plants.
FAQ
A planted bamboo tree may take 3-4 years to grow to its full height. But some species of the plant can grow as fast as 36 inches per 24 hours.
Cut 10 inches of a bamboo plant. Add it to water and refresh it bi-daily. When you get roots of 2 inches or more move it to a planting pot.
Lucky bamboo grows in water with little care. Make sure the container is big enough for the plant to grow. Change the water weekly. Keep it away from direct sunlight.
Related reading:
Table of Contents





