Last updated on
Greenhouse enthusiasts should consider grain bin greenhouses because of their potential to provide sustainable, efficient, and cost-effective solutions for year-round gardening.
I have created these unique designs for your inspiration. I hope you will enjoy them!
Though the internet is brimming with ideas on grain bin greenhouses, our quest is to explore the uncharted territory, identify new angles, and bring a fresh perspective to the table.
While we will include resources for the popular, tried-and-true ideas, our focus will be on cultivating a list of unique proposals that could revolutionize this space.
Our aim? To inspire your creativity, ignite your imagination, and make your grain bin greenhouse project notably unique.
Let’s dive right in!
Turning a Grain Bin Into a Biotecture Greenhouse
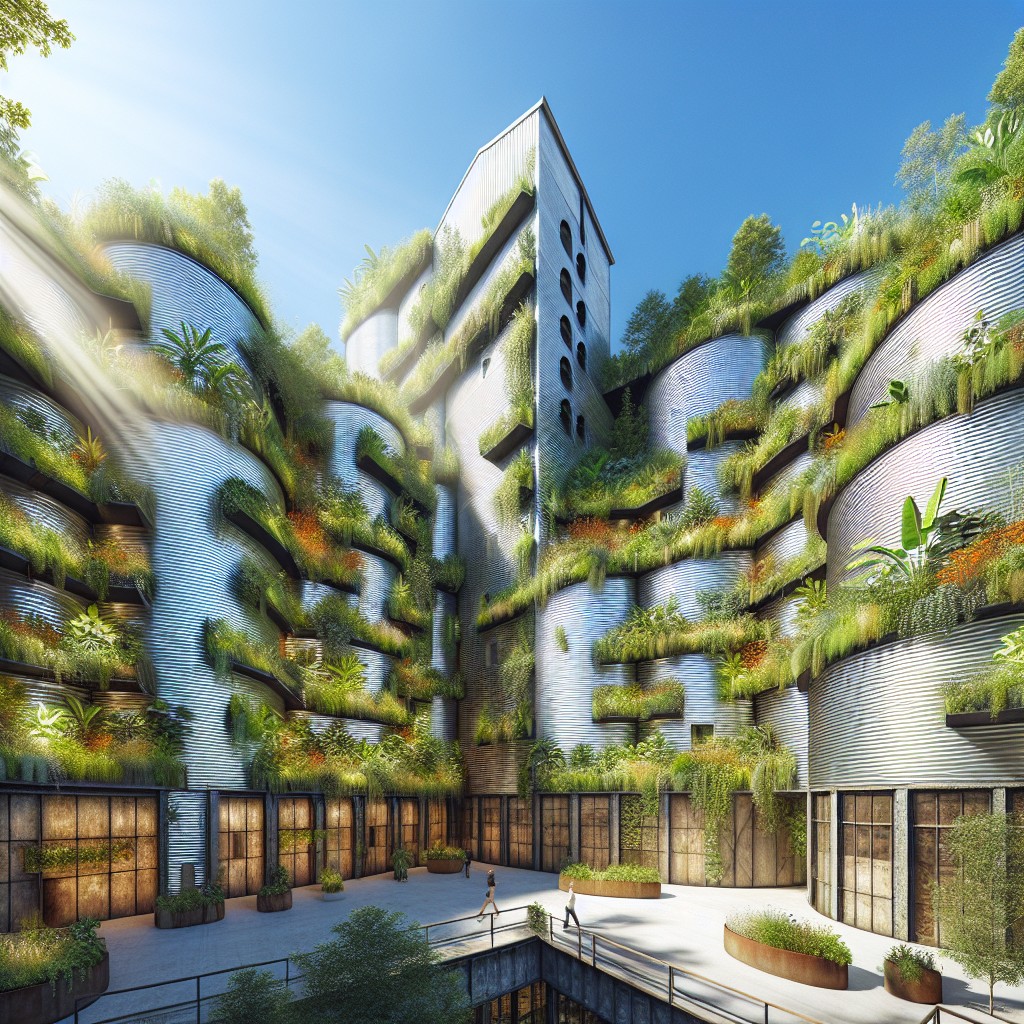

Recycling old grain bins by re-purposing them into greenhouses creates a sustainable and efficient growing environment often referred to as a biotecture greenhouse. This approach fuses biological considerations with architecture, promoting eco-friendly practices such as reducing waste and harnessing natural energy sources.
To achieve this, certain modifications are necessary:
- Insulation: Grain bins are typically made of metal, which can conduct heat rapidly. For effective temperature regulation, proper insulation using materials like foam, straw bales, or even recycled fabric can help stabilize internal temperatures.
- Glazing: Replace sections of the grain bin wall with transparent materials like polycarbonate panels to allow sunlight to penetrate, fostering plant growth and harnessing solar energy.
- Ventilation: Even in a sealed metal structure, maintaining air quality is essential. Implement a ventilation system that can be manually or automatically controlled to manage humidity and prevent overheating.
- Aquaponics: Incorporate a symbiotic system combining aquaculture with hydroponics to efficiently use space and resources within the greenhouse. Fish waste provides an organic nutrient source for the plants, which in turn purify the water for the fish.
These foundations establish the environmental synergy at the heart of a biotecture greenhouse, balancing the needs of the structure with the living ecosystem within.
How to Incorporate Hydroponics in a Grain Bin Greenhouse
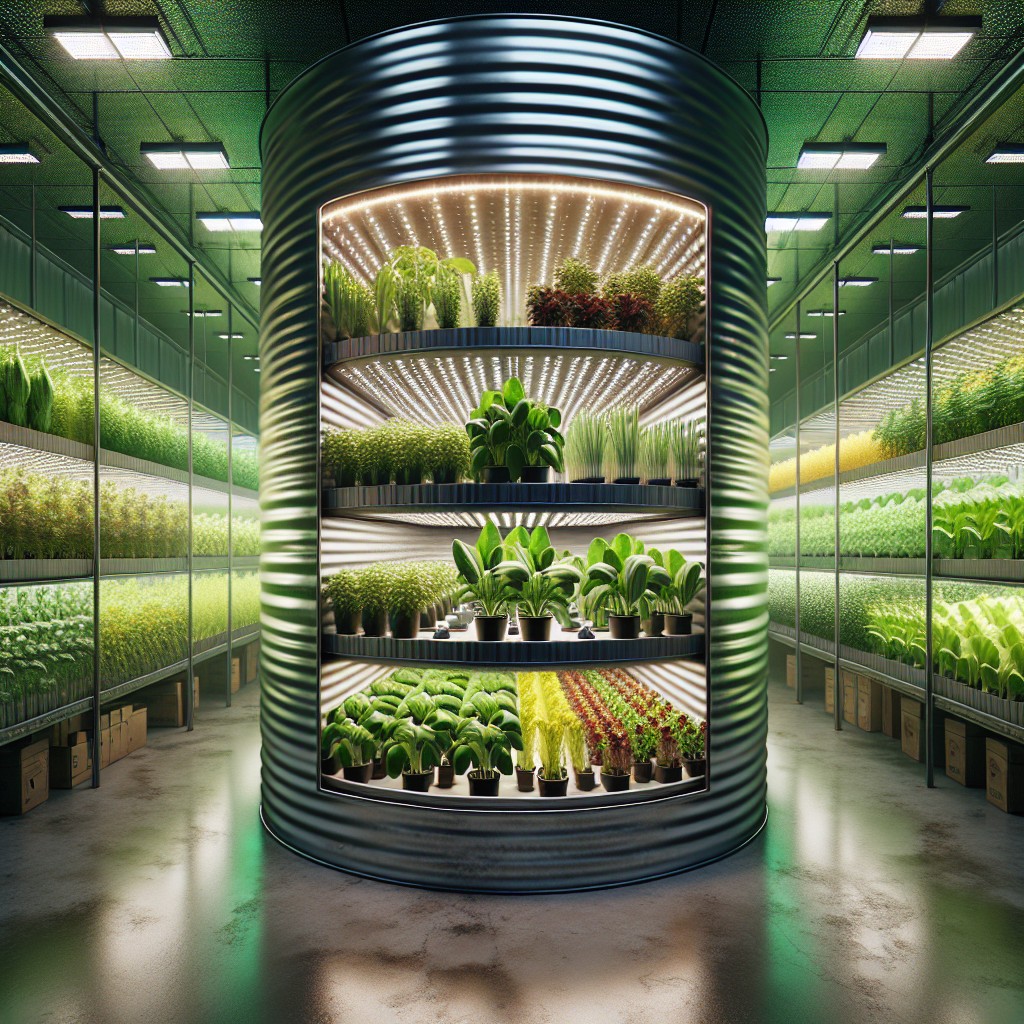

Implementing a hydroponic system inside a grain bin greenhouse combines modern agriculture with resourceful repurposing. To get started:
- Measure the interior diameter to determine the available space for hydroponic setups. Use circular or radial designs to complement the bin’s shape.
- Choose a hydroponic system that suits your plant selection and expertise level: wick systems for beginners, nutrient film techniques for leafy greens, or aeroponic systems for tech-savvy gardeners.
- Install grow lights to ensure plants receive adequate light, particularly in the upper levels of the bin if using vertical hydroponics.
- Insulate the grain bin properly to maintain temperature and humidity levels vital for hydroponic plant health.
- Set up water tanks and pumps outside the greenhouse if space is limited inside, and use insulated pipes to prevent water temperature fluctuations.
- Monitor pH and nutrient levels regularly with simple testing kits to ensure optimal plant growth.
- Consider using a vertical hydroponic system to maximize the vertical space unique to a grain bin’s structure, allowing for more growth area.
- Utilize the curved walls by installing custom curved shelving that fits snugly against them, making the most of the available space.
Tips to Maximize Space in a Silo Greenhouse
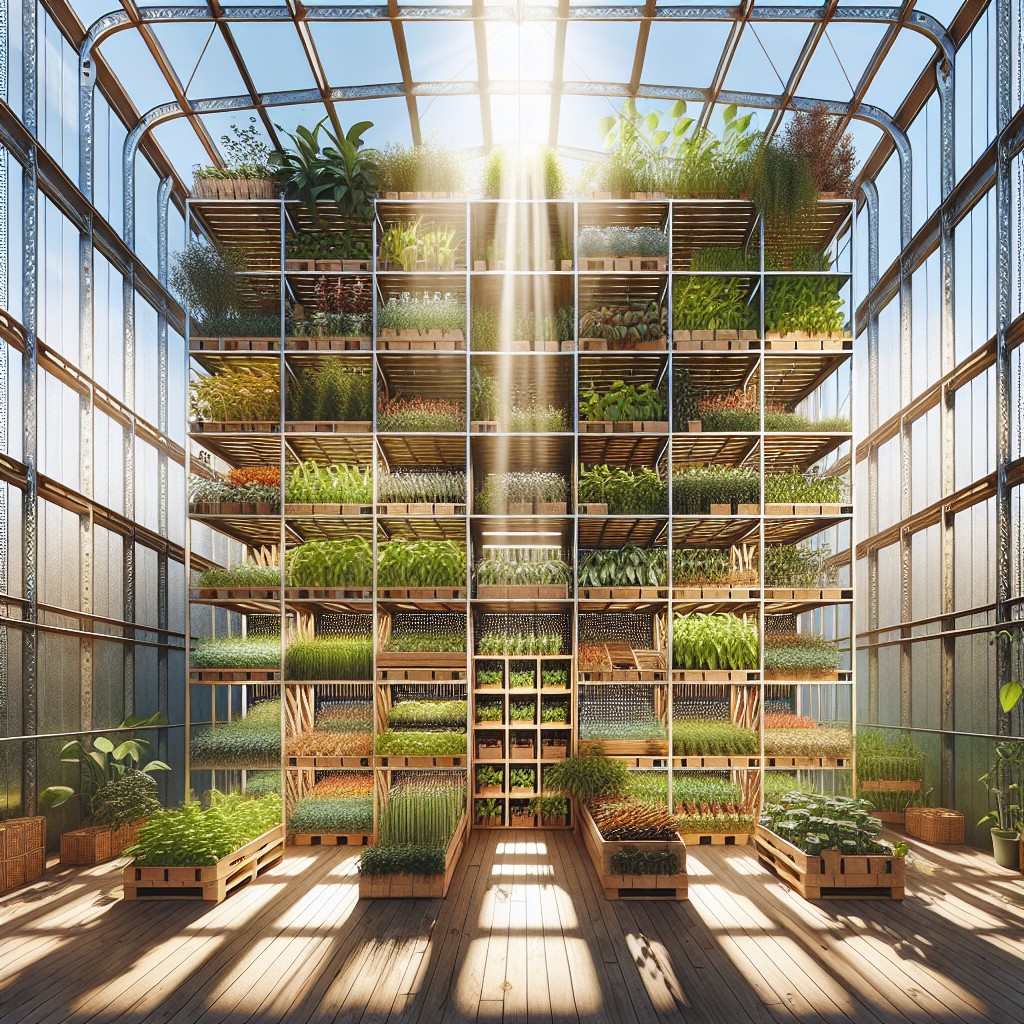

Embrace Vertical Gardening: By implementing vertical gardening techniques such as using hanging planters and shelves, you can cultivate plants at multiple levels within the silo’s tall structure, thereby utilizing vertical space efficiently.
Choose Compact Varieties: Opt for dwarf or bushier plant varieties that require less room to grow. This way, you can fit more plants into your available space without overcrowding.
Rotate Crops: Practice crop rotation to make the most of the growing seasons. By selecting plants with different growing periods, you can continuously harvest and replant areas, keeping the greenhouse productive all year round.
Incorporate Climbing Plants: Take advantage of the silo’s curved walls by growing climbing plants like beans or cucumbers. Set up trellises or support wires where vines can ascend, creating a natural green wall and saving valuable floor space.
Utilize the Center: Position taller plants and trees in the center of the silo and shorter plants around them. This helps optimize sunlight distribution and maximizes the amount of produce you can grow.
Implement Succession Planting: Sow seeds in intervals, ensuring that not all plants need to be harvested at the same time. This staggered approach keeps space in constant use and can lead to a more efficient greenhouse.
Smart Layout Planning: Carefully plan the layout to include walkways and spaces for equipment without compromising the area needed for planting. Efficient spatial organization ensures you have comfortable access to all plants for maintenance and harvesting.
Inexpensive Heating Systems for Grain Bin Greenhouses
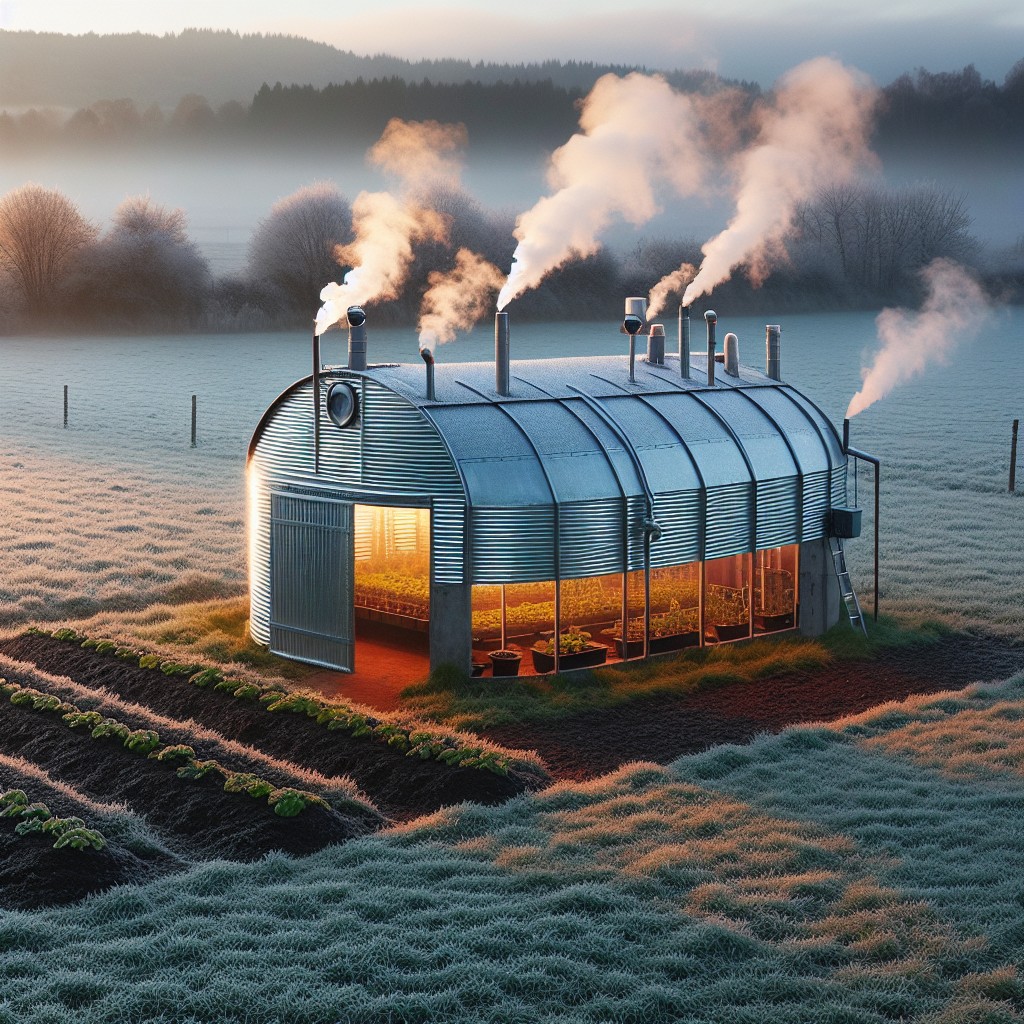

Harness the power of passive solar heating by strategically placing your grain bin greenhouse to maximize sunlight exposure during the day. Adding thermal mass, such as water barrels or concrete, can absorb heat when the sun is up and release it slowly as temperatures drop.
Composting within your space creates a dual-purpose system: decomposing organic matter generates heat while providing nutrient-rich soil for your plants. This method encourages a sustainable cycle within your greenhouse.
Rocket mass heaters offer an efficient wood-burning option. These systems burn small amounts of wood at high temperatures, which translates to less fuel and sustained heat through a thermal mass, such as a cob bench or earthen floor.
Solar air heaters can be crafted from repurposed materials such as aluminum cans or metal sheets painted black. They absorb solar energy and circulate warm air throughout the structure.
For localized heating, consider soil heating cables or mats. These systems gently warm the root zones of plants, boosting their growth without the need to heat the entire airspace of your grain bin.
Explore the option of biogas digesters if you have access to organic waste. They convert waste into methane gas which can be used as a heat source, offering a self-sufficient solution to your heating needs.
Using Solar Panels On Your Grain Bin Greenhouse

Harnessing solar energy is a strategic move to power your greenhouse sustainably. With the circular design of grain bins, solar panels can be installed either on the roof or on nearby ground-mounted systems, ensuring that space is used efficiently and aesthetically.
Integration with the Structure:

- The curved surface requires flexible solar panels that can conform to the bin’s shape.
- Roof-mounted panels should be positioned to capture maximum sunlight, typically facing south in the Northern Hemisphere.
- Consider using mounting brackets that allow for angle adjustments to optimize seasonal solar capture.
Energy Considerations:

- Calculate your greenhouse’s energy needs to determine the size of the solar array required.
- Excess energy generated can be stored in batteries or fed back to the grid, depending on local regulations.
Electrical Setup:

- Inverters are necessary to convert the DC electricity from solar panels into AC for greenhouse use.
- Ensure waterproof and weatherproof conduits are used to protect electrical connections.
Cost and Payback Period:

- Assess the initial investment against long-term benefits, including possible tax incentives and reduced utility bills.
- Payback period can vary, but the reduction in operating costs generally offsets the expense over time.
Maintenance:

- Regular cleaning of solar panels ensures efficiency is not compromised by dust or debris.
- Inspect electrical systems periodically to prevent power disruptions.
By utilizing solar panels, your grain bin greenhouse can operate more independently of non-renewable resources, contributing positively to both your carbon footprint and operational expenses.
Which Plants Grow Best in a Grain Silo Greenhouse?
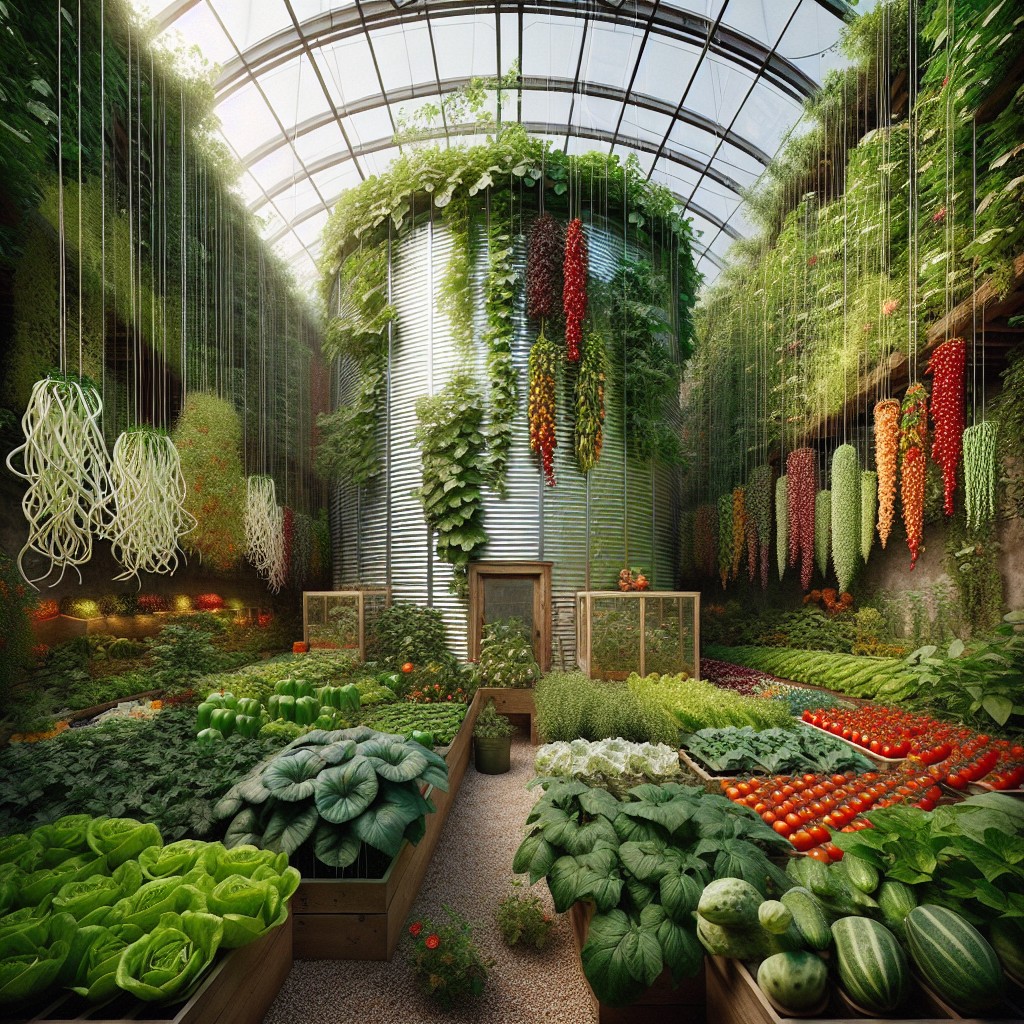

In the unique environment of a grain silo greenhouse, plant selection is key to successful growth. Opt for varieties that thrive in warm, humid conditions, as these greenhouses can retain more heat than traditional structures. Leafy greens like spinach, kale, and lettuce are ideal due to their lower light and space requirements. Herbs such as basil and cilantro also flourish, providing fresh flavors at your fingertips.
Tomatoes and peppers are well-suited to the vertical space a silo provides, while cucumbers can be trained to climb, making efficient use of the circular area. For those interested in year-round gardening, consider cold-tolerant plants like Swiss chard and bok choy during cooler months.
Keep in mind, pollination can be a challenge in an enclosed space, so selecting self-pollinating or wind-pollinated plants, or introducing pollinators, can be beneficial. Always monitor moisture levels to prevent excess humidity from promoting plant diseases.
Above all, adapt your plant choices to match the light intensity available in your silo setup. By tailoring your selection to your specific environment, you can enjoy a bountiful harvest from your silo greenhouse.
How to Maintain Temperature in a Grain Bin Greenhouse
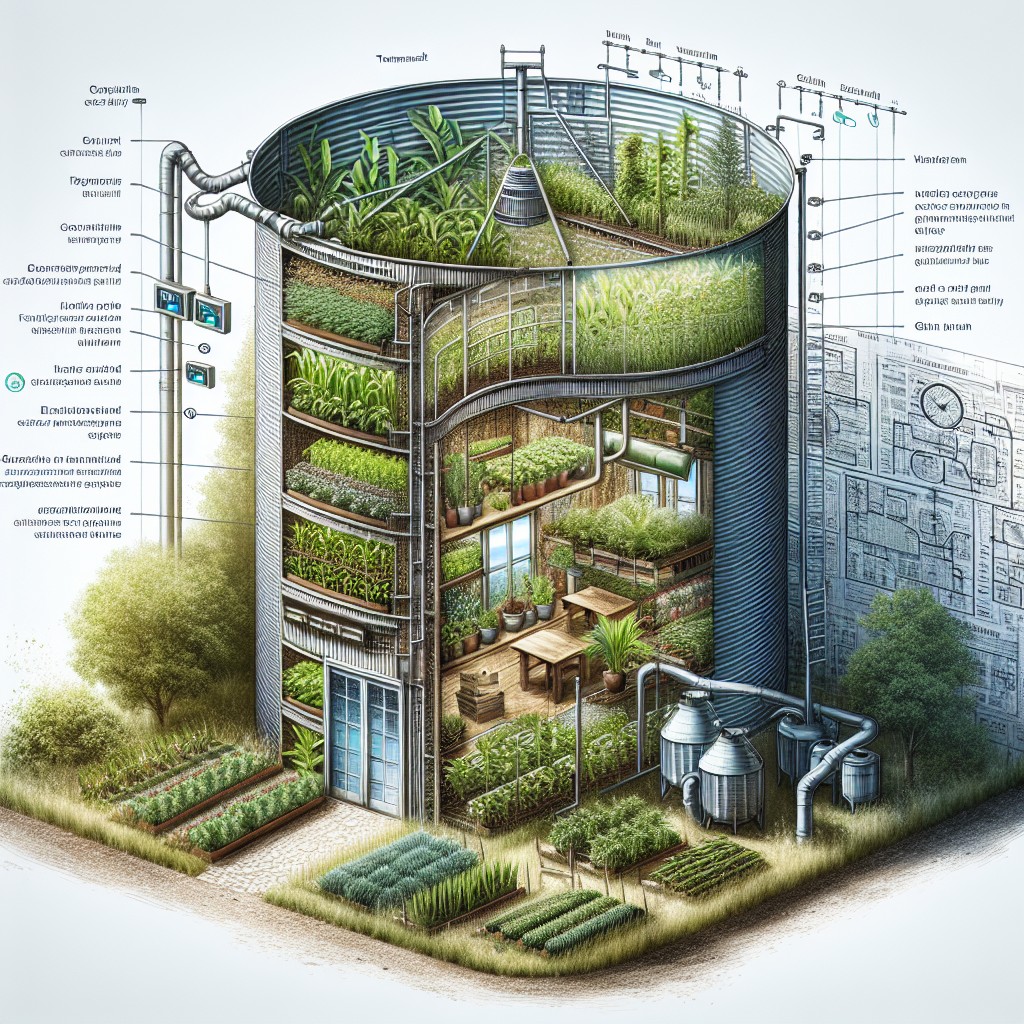

Maintaining an optimal temperature in your grain bin greenhouse is crucial for plant health and energy efficiency. Here are some practical ways to regulate the internal climate:
Insulation: Start with proper insulation to prevent heat loss. Use insulated panels or spray foam to cover the interior walls and ceiling. Remember, the circular shape of grain bins provides a natural advantage in maintaining temperatures due to less surface area exposed to outdoor temperature fluctuations compared to traditional greenhouses.
Thermal Mass: Incorporate materials with high thermal mass inside the greenhouse to stabilize temperatures. Water barrels, rocks, or concrete can absorb heat during the day and release it slowly at night, reducing the need for additional heating.
Ventilation: Install operable vents or windows towards the top and bottom of the structure. Heat rises, so letting hot air escape from the top while drawing in cooler air from the bottom can create a self-regulating effect.
Shading: During the hotter months, use shade cloths or external shutters to prevent overheating. These can be retractable or removable to adjust for seasonal changes.
Heating Systems: For cold climates, consider installing a small wood stove, pellet stove, or passive solar heaters. These can provide a cost-effective heating source and add to the greenhouse’s sustainability.
Temperature Monitoring: Use a reliable thermometer or a digital climate control system to continuously monitor conditions. This will help you make timely adjustments and ensure a consistent environment for your plants.
Each strategy contributes to creating a balanced atmosphere inside your grain bin, mitigating temperature extremes without relying heavily on electrical heating or cooling systems.
Grain Bin Greenhouse: DIY Vs Professionals

Deciding whether to undertake the conversion of a grain bin into a greenhouse as a do-it-yourself project or to enlist professional help hinges on several factors. DIY enthusiasts may embrace the hands-on approach due to the potential cost savings and the personal satisfaction of completing a project independently. However, it requires a solid grasp of construction principles, patience, and a willingness to learn new skills. Critical aspects like creating suitable doorways, installing transparent panels for sunlight, and ensuring structural stability call for meticulous attention to detail.
On the other hand, hiring professionals offers the advantage of experience and expertise. Specialists in greenhouse constructions can navigate complex areas such as climate control systems, proper sealing techniques, and optimized plant layouts. They can also ensure compliance with building codes and regulations, which is crucial for safety and legality. While this option raises the project budget, it minimally impacts daily life and provides a quicker turnaround, allowing your greenery to thrive sooner. Choosing this path also typically includes the benefit of warranties and professional follow-up on the installation.
Weigh time commitments, skill level, project scale, and budget when deciding between DIY or professional involvement. Each choice carries unique benefits, and the best path forward will align with your individual preferences and circumstances.
Insulating Your Grain Bin Greenhouse for Winter

Ensuring your grain bin greenhouse remains warm during winter requires effective insulation to minimize heat loss. Reflective insulation can be installed on the interior walls to retain warmth, as it reflects heat back into the space. Rigid foam or fiberglass batts between the grain bin ribs serve well for added thermal resistance. For a more sustainable approach, consider using natural insulations like wool, cotton, or recycled denim.
The floor is a significant area of heat loss; therefore, insulating it with a thick layer of rigid foam beneath your growing platform is essential. Additionally, installing a double-layer plastic film across the greenhouse’s frame can create a layer of insulating air, reducing the escape of warmth. Seal gaps around doors and windows with weather stripping and use insulated doors to prevent drafts. Remember, maintaining temperature stability is crucial for plant health and energy efficiency. Employing these strategies will ready your grain bin greenhouse for the colder months.
Silo Greenhouse: Rainwater Collection Systems

Rainwater collection is an eco-friendly method to supply your greenhouse with water. The cylindrical shape of a silo naturally directs rainfall downwards, making it ideal for harvesting rainwater.
Install gutters along the edges to channel water into a storage tank or barrel. Choose a dark, food-grade container to prevent algae growth and place it at a higher elevation to use gravity for water distribution. Incorporate a filtration system to remove debris before storage.
For irrigation, a simple drip system can be connected to your tank to deliver water directly to the plants’ roots, conserving this valuable resource and reducing water bills. Regularly check for blockages and clean gutters to maintain efficiency.
Pest Control in a Grain Bin Greenhouse

Keeping your greenhouse free from pests without the use of harsh chemicals is crucial for a healthy harvest and environment. Start with prevention; fine mesh screens on vents and doors deter insects while still allowing air flow. Companion planting can attract beneficial predators or repel harmful insects—marigolds, for example, are great insect repellents.
Introduce biological controls by releasing predator insects like ladybugs or lacewings which feast on common pests such as aphids. For more targeted issues, consider pheromone traps that lure and capture specific pest species without affecting beneficial insects.
Regularly inspect plants for early signs of infestation. Look under leaves and around stems for any unusual activity. Should pests become a problem, insecticidal soaps and neem oil offer organic solutions that are effective yet gentle on plants.
Ensure cleanliness by removing plant debris and disinfecting tools; pests love to hide in decaying plant matter. By being vigilant and employing these strategies, you can protect your grain bin greenhouse from unwanted guests and promote a thriving, eco-friendly garden.
Lighting Solutions for a Grain Bin Greenhouse

Natural sunlight is the primary source of light for plants in a grain bin greenhouse, but optimizing plant growth year-round may require supplemental lighting. Consider these points when designing your lighting strategy:
- LED grow lights are energy-efficient and offer a broad spectrum of light suited for different growth stages.
- Position lighting strategically to reach all plants evenly, avoiding shadowed areas that could inhibit growth.
- Utilize light timers to maintain consistent day and night cycles, mimicking natural light patterns.
- Explore options for solar-powered lights to maintain sustainability and reduce energy costs.
- Reflective interior surfaces can enhance light distribution, ensuring that plants receive ample light from all angles.
- Look into overhead and vertical lighting systems which can be tailored to the unique cylindrical space of a grain bin greenhouse.
By integrating these lighting solutions effectively, you can ensure robust plant growth and productivity within your silo greenhouse.
Retractable Shades for Grain Silo Greenhouses

Managing sun exposure is crucial for plant health, especially in a unique structure such as a converted grain silo. Retractable shades offer a practical solution by allowing customizable light control throughout the day and across seasons.
Flexibility of Light Adjustment: You can extend or retract the shades to cater to different plant species’ light needs or to respond to changes in weather.
Energy Efficiency: By using shades to control temperature naturally, you reduce reliance on electric heating or cooling systems, which aligns with sustainable farming practices.
Ease of Installation: Various retractable shade systems are designed for straightforward installation, ensuring they can be fitted within the circular shape of a grain bin without complex modifications.
Durability & Maintenance: Select materials that withstand the greenhouse environment’s humidity and temperature variations with minimal maintenance requirements.
Retractable shades seamlessly integrate into a grain bin’s structural framework, offering a simple yet effective method to optimize growing conditions for a thriving greenhouse.
Cooling Systems Suitable for Grain Bin Greenhouses

Cooling your greenhouse effectively is crucial during warmer months to prevent plant stress and overheating. Passive ventilation can be a low-cost and energy-efficient option, using strategically placed vents and doors to create a natural airflow.
Evaporative coolers add moisture to the air while dropping temperatures significantly by pulling warm air through water-saturated pads. For a grain bin greenhouse, install the cooler on the side that receives prevailing winds for optimum effect.
Shade cloths provide a straightforward solution to reduce heat. Opt for a cloth with the correct density for your plants’ light needs and affix it above the roof or on the sides during the hottest part of the day.
Reflective insulation also helps by reflecting sunlight away from your greenhouse. It can be fitted against the interior walls and ceiling to reduce the amount of heat that’s absorbed by the structure.
For an active cooling system, exhaust fans can be installed to pull hot air out of the grain bin greenhouse. These should be placed at the top, where the hottest air will collect, to be most effective.
Lastly, a simple misting system can lower temperatures while providing hydration to plants. Install a network of nozzles to create a fine mist which cools the surrounding air as it evaporates.
Choosing the right combination of these cooling methods can maintain a pleasant temperature inside your grain bin greenhouse even when exterior temperatures climb.
Storing Harvest in a Grain Bin Greenhouse

Maximizing your grain bin greenhouse for storage after the harvest requires strategic planning. Given that space can be at a premium, consider installing shelving units along the inner wall, making sure they don’t block sunlight for living plants.
Utilize vertical space efficiently with hanging baskets or netting for crops like garlic or onions that benefit from airflow during drying.
For root vegetables such as carrots and potatoes, use stackable bins with breathable materials and ensure they’re kept in a cool, dark section of the greenhouse to prevent spoilage.
Temperature control is crucial; maintain a consistent environment with the help of a thermostat and adequate insulation.
Remember that some crops can continue to ripen post-harvest, so creating separate zones within your storage area can minimize ethylene exposure to sensitive produce.
Lastly, for high-humidity items, incorporate moisture control solutions to keep mold and rot at bay, ensuring your harvest is well-preserved for future use.
How to Make a Grain Bin Greenhouse Portable

To achieve portability for your grain bin greenhouse, consider the following:
- Install on a trailer: A sturdy trailer can serve as the foundation, ensuring your greenhouse can be towed to different locations as needed.
- Skid-mounted design: Use heavy-duty skids if you prefer a setup that can be moved with equipment like tractors or trucks.
- Modular setup: Create a design that allows for disassembly into panels or sections. This way, it can be broken down, transported, and reassembled without permanent alterations to the structure.
- Lightweight materials: Use materials such as polycarbonate panels for the walls and roof instead of heavier options to reduce the overall weight and facilitate easier movement.
- Anchor safely: Even when aiming for portability, it’s crucial to securely anchor your greenhouse at each new site to protect against wind and weather.
- Plan for utilities: Consider solar power for energy, and portable water tanks for irrigation to ensure your greenhouse remains functional even on the move.
These considerations will ensure your grain bin greenhouse remains versatile and adaptable to changing needs or locations.
Using a Grain Bin Greenhouse for Urban Farming

Urban farming transforms city landscapes, encouraging sustainability and local produce growth. Grain bin greenhouses offer a viable solution for space-constrained urban environments, enabling residents to cultivate a variety of crops year-round.
These structures can be erected on small lots or even rooftops, providing an excellent use of vertical space.
In these settings, grain bin greenhouses serve several functions:
- They act as a focal point for community engagement and education about agriculture and sustainability.
- The circular design is inherently strong and wind-resistant, making it suitable for areas with limited space and higher exposure to urban elements.
- The metal walls can be painted with reflective or light colors to minimize heat absorption in hot climates, conserving energy.
- With their compact footprint, these greenhouses can be integrated into urban designs, including parks, schools, or community centers, maximizing underutilized spaces.
Coupling grain bins with urban agriculture techniques, such as rooftop gardens or hydroponics, enhances food security and reduces carbon footprints by minimizing the distance food travels from farm to table.
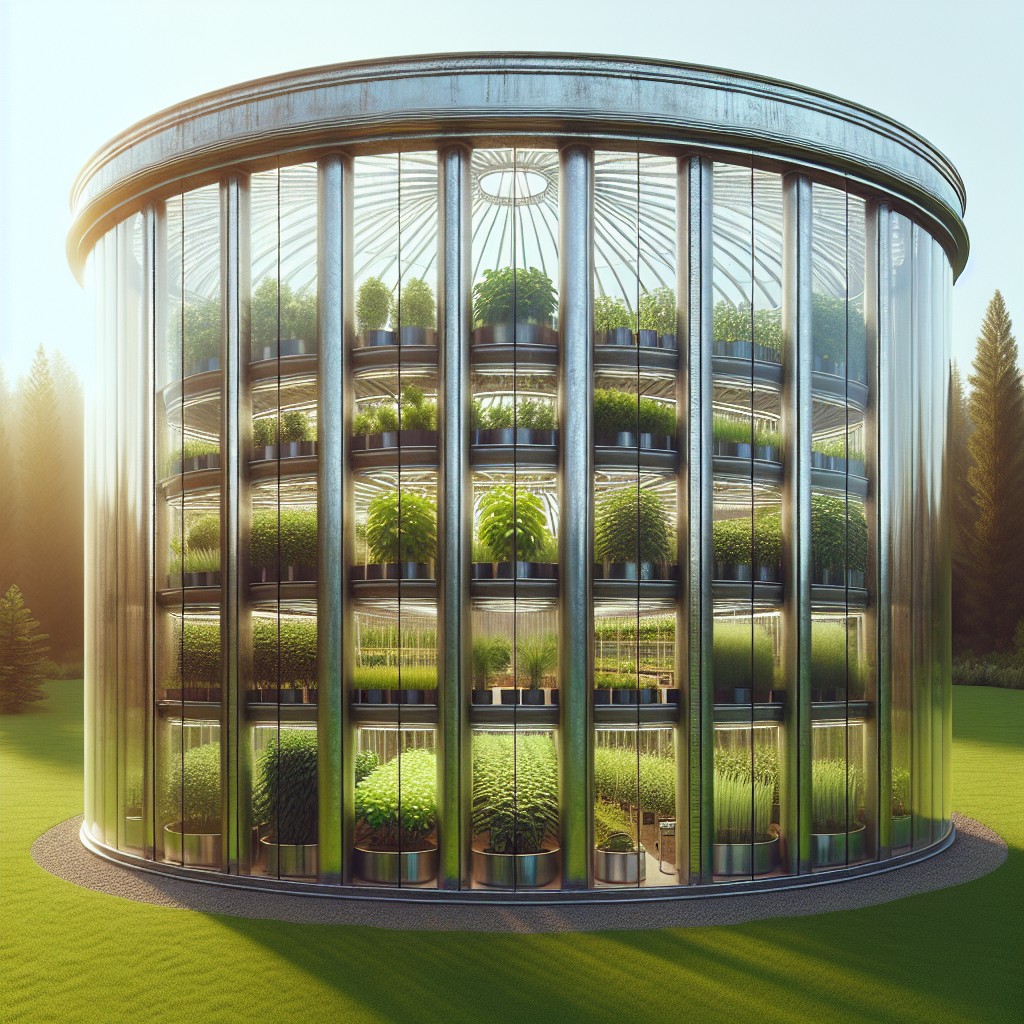
Silo Greenhouse and Vertical Gardening: A Perfect Match

Vertical gardening elevates the productivity of a silo greenhouse by exploiting the circular design and height. The curvature of the bin walls naturally supports trellising systems for climbing plants.
Implement stackable planters or hanging baskets to take advantage of available air space, creating layers of greenery that enhance the microclimate. Optimize grow lights by positioning them at strategic points, ensuring even distribution of light for all plants, regardless of height.
This technique maximizes the use of limited ground space, allowing for a diverse range of crops within a single structure, and encourages efficient air circulation, crucial for plant health and pest reduction. Integrating vertical elements transforms a grain bin into a thriving agricultural tower.
Smart Technologies for Grain Silo Greenhouses

Integrating smart technologies into your grain bin greenhouse can elevate its efficiency and productivity. Here are some ways to include modern tech:
Automation
Automated systems can regulate watering, lighting, and temperature, adapting to real-time conditions. They reduce manual labor and help maintain optimal growth environments.
Sensors
Install sensors to monitor humidity, soil pH, and nutrient levels. These devices provide valuable data, enabling precise adjustments for plant health.
Climate Control
Climate control systems connected to smart devices allow for remote regulation of the greenhouse’s internal environment from your smartphone or computer.
LED Grow Lights
Energy-efficient LED grow lights can be synced with smart timers to simulate natural light cycles, promoting effective plant growth while saving on electricity.
App Integration
Use applications that integrate all your smart devices for an easy-to-use centralized control panel. This helps you oversee all aspects of your greenhouse in one place.
Data Analytics
Harness the power of data analytics to track plant growth trends, predict yields, and make informed decisions about crop rotation and planting schedules.
Using Recycled Materials for Grain Bin Greenhouse Construction

Embracing recycled materials not only bolsters your environmental stewardship but can also cut costs significantly. Here’s how you can incorporate such materials in your build:
- Insulation: Old denim or newspapers can be processed into insulation. This eco-friendly alternative performs well, keeping your greenhouse warm without the ecological footprint of traditional insulators.
- Windows: Source discarded windows from renovation sites or second-hand stores. These can help foster a patchwork aesthetic while ensuring ample sunlight enters your greenhouse.
- Watering System: Channel creativity by using repurposed plastic bottles or old gutters to create an irrigation system, minimizing water waste and reducing the need for new plastics.
- Flooring: Reclaimed wood or leftover tiles can provide durable and unique flooring options that contribute to the visual charm of the space.
- Shelving: Discarded pallets or old ladders can be transformed into rustic shelving, ideal for organizing plants and maximizing vertical space.
- Planters: Instead of purchasing new pots, turn to used buckets, tubs, or even tires for a quirky, resourceful way to contain your plants.
Each repurposed item not only saves it from the landfill but also lends a story and character to your greenhouse, making it as sustainable as it is special.
Ideas Elsewhere
- https://sanitred.com/how-to-build-grain-bin-house-silo-home/
- https://thetinylife.com/grain-silo-house/
- https://permies.com/t/75239/Grain-Bin-Building-Idea
Table of Contents