Last updated on
Modern problems require modern solutions. As architects dwell on aligning their designs with the imperative of sustainability without compromising durability and energy efficiency, many access doors introduce a different perspective on fulfilling function while contributing to sustainable, durable, and energy-efficient structures.
Let’s explore how an access door’s sustainability, durability, and energy efficiency make it essential in green building systems.
The Essence of Green Building Systems
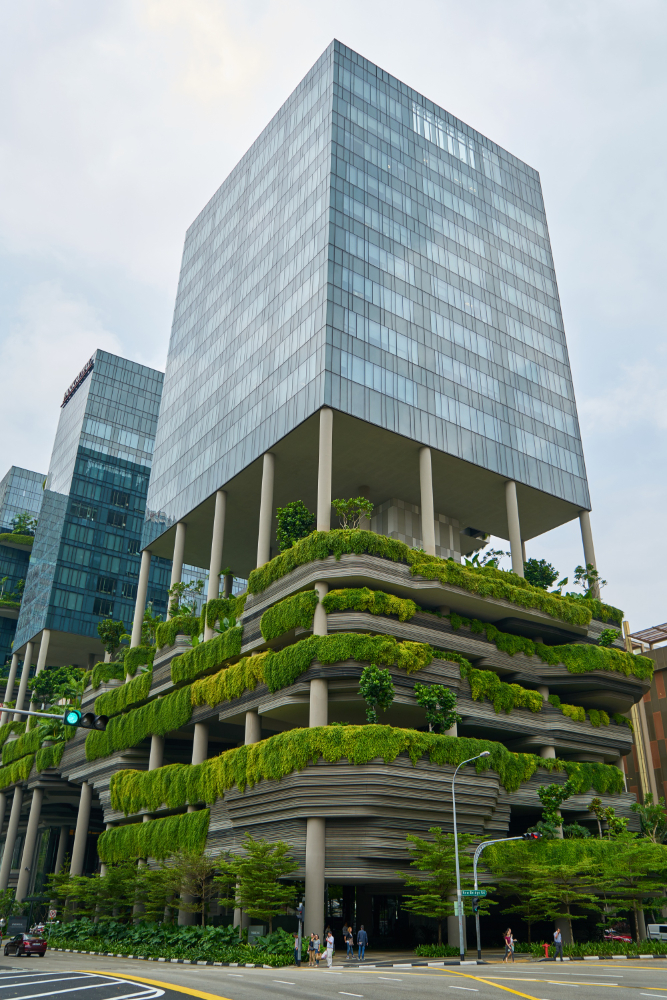

Green building systems are an essential part of modern construction. These systems have changed how we construct buildings by following specific principles and objectives. They aim to redefine how buildings interact with the environment.
1. Principles of Green Building
Green building prioritizes sustainability. This entails using renewable resources, energy-efficient designs, and environmentally friendly materials. Green practices aim to preserve natural resources and promote long-term environmental health by minimizing a building’s ecological footprint.
2. Energy Efficiency and Conservation
Green building systems aim to use less energy by using smart designs, better insulation, and renewable energy sources. This reduces greenhouse gas emissions, which is important to address climate change.
3. Materials and Resources
Green building emphasizes using environmentally friendly materials. This includes recycled, reclaimed, or locally sourced materials, reducing the environmental impact of extraction, manufacturing, and transportation.
4. Water Efficiency
Green building practices prioritize water efficiency. To save water, you can install less water fixtures, collect rainwater, and design your landscape to reduce water usage. The goal is to conserve water resources and enhance overall water management.
5. Indoor Quality
Green building systems prioritize the well-being of occupants by promoting superior indoor environmental quality. This encompasses proper ventilation, optimal lighting, and non-toxic materials to create healthier and more comfortable living and working spaces.
6. Waste Reduction and Recycling
Green building minimizes construction waste through efficient design and recycling initiatives. This reduces the environmental impact of construction activities, promoting a circular economy where materials are repurposed and reused.
7. Certification Standards
Numerous certification standards, such as LEED, provide a framework for evaluating and recognizing green building initiatives. Achieving certification signals a commitment to sustainable practices and serves as a benchmark for industry excellence.
8. Cost-Effective Long-Term Solutions
Green buildings are expensive initially, but they offer long-term benefits worth the investment. Energy savings, lower operating costs, and higher property values make green buildings economically viable.
9. Global Impact and Future Trends
Green building practices contribute significantly to global sustainability goals. As the construction industry evolves, emerging trends such as smart building technologies, biophilic design, and regenerative architecture further shape the future of green building.
Sustainability, Durability, and Energy Efficiency in Access Doors

Access doors are an important part of constructing sustainable buildings. They are durable, energy-efficient, and responsible for reducing the environmental impact, like the BA-FRI-SS fire rated access panel insulated in stainless steel. These doors are crucial for creating buildings that can last a long time while being environmentally friendly.
1. Sustainably Sourced Materials
Access doors crafted from sustainably sourced materials align with the ethos of sustainable construction. Utilizing renewable resources or recycled materials minimizes the ecological footprint, contributing to environmentally conscious building practices.
2. Durability as a Sustainability Pillar
Durability is a cornerstone of sustainable construction. This approach promotes a more sustainable way of maintaining buildings by saving resources and minimizing construction waste.
3. Energy-Efficient Designs
Access doors with energy-efficient designs, including proper insulation, contribute to a building’s overall energy efficiency. These doors help keep indoor temperatures consistent, which means less need for heating or cooling systems and lower energy use.
4. Sealing and Weatherproofing
Well-designed access doors enhance the building envelope. Proper sealing and weatherproofing prevent air leakage, creating a more efficient thermal barrier. This improves energy performance and reduces the building’s carbon footprint.
5. Recyclability and End-of-Life Considerations
Recyclable access doors are part of a circular economy. By using materials that are recyclable at the end of their life cycle, construction projects can minimize environmental impact.
6. Sustainable Manufacturing Practices
Choosing access doors from manufacturers committed to sustainable practices further amplifies their impact. Manufacturers employing eco-friendly production processes and minimizing resource consumption contribute to a more sustainable supply chain.
7. Adaptable and Future-Ready Designs
Access doors designed with adaptability contribute to sustainability. Their ability to adapt to new technology and building systems ensures that they stay up to date, which means fewer replacements. This promotes a sustainable and long-term construction strategy.
The Takeaway
As architects and builders navigate the intricate landscape of sustainable construction, access doors are beacons of innovation. In their seemingly simple existence, they hold the power to shape a future where buildings seamlessly blend functionality with environmental responsibility.
Each access door becomes a testament to a commitment— not just to open and close, but to sustain, endure, and lead the way in crafting a greener, more resilient built environment.
Table of Contents