Last updated on
Asbestos, a naturally occurring mineral known for its heat resistance and durability, was once extensively used in construction and manufacturing. However, due to its proven association with serious health risks, including lung cancer and mesothelioma, the use of asbestos has significantly decreased over the years.
Despite regulatory efforts to ban or limit its usage, asbestos can still be found in various environments, posing a potential threat to human health. Asbestos testing plays a crucial role in identifying and managing the presence of this hazardous material, ensuring the safety of individuals and communities.
Unveiling Hidden Threats
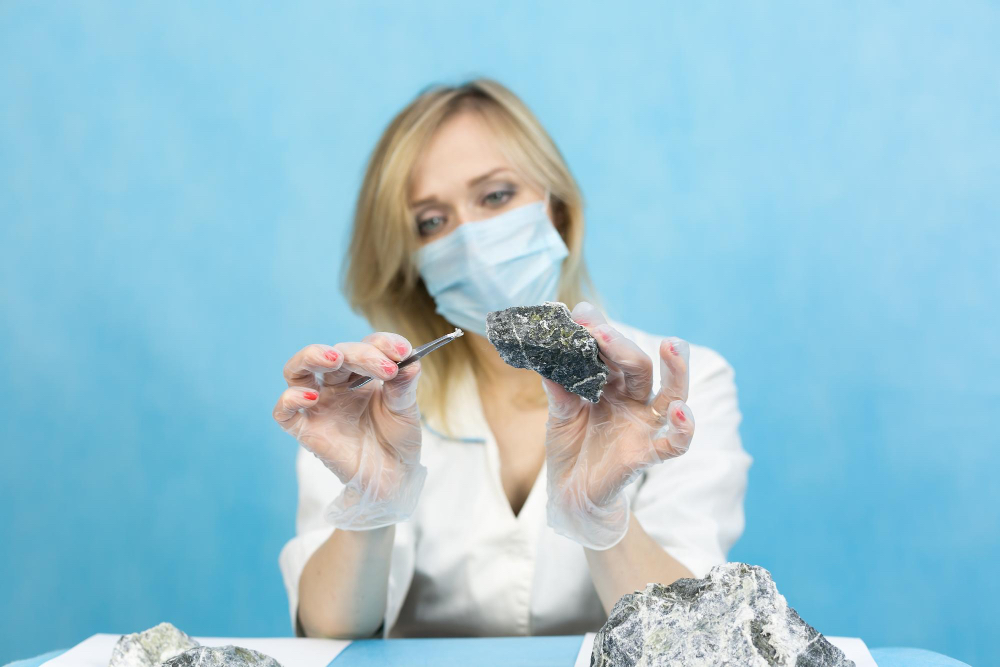

Industrial settings are notorious for their historical use of asbestos in various applications, such as insulation, fireproofing, and machinery components. Asbestos-containing materials (ACMs) in these environments may become friable over time, releasing asbestos fibers into the air.
As a result, workers in industrial facilities face an elevated risk of asbestos exposure. Testing for asbestos in industrial environments involves a comprehensive assessment of building materials, machinery, and air quality.
Specialized testing methods, including polarized light microscopy and transmission electron microscopy, are employed to accurately identify asbestos fibers. Regular testing and monitoring are imperative in these settings to ensure compliance with safety regulations and protect the well-being of workers.
Safeguarding Homes from Silent Threats
While the use of asbestos in residential construction has significantly decreased since the late 20th century, many older homes still contain asbestos-containing materials. Common sources of asbestos in residential buildings include insulation, floor tiles, and roofing materials.
As these materials age or undergo renovations, asbestos fibers may be released into the air, posing a risk to the occupants. Asbestos testing in residential environments involves inspecting potential ACMs, collecting samples, and analyzing them in accredited laboratories.
This proactive approach helps homeowners identify and address asbestos-related hazards, whether through removal, encapsulation, or other appropriate management strategies. By ensuring the safety of residential spaces, asbestos testing contributes to creating healthier living environments for families.
Asbestos in the Natural World
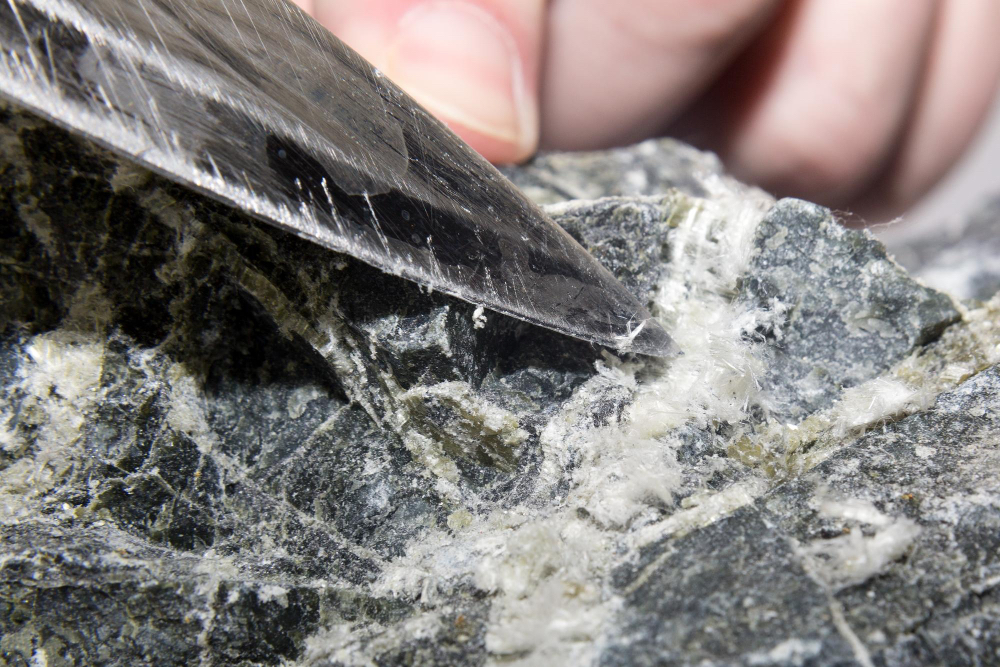

Beyond industrial and residential settings, asbestos can also be found in the natural environment. Certain geological formations contain asbestos deposits, leading to the potential release of fibers into the air, water, or soil. Mining activities, weathering of asbestos-rich rocks, or human-made disturbances can exacerbate the dispersion of asbestos fibers into the environment.
Asbestos testing in natural settings involves monitoring air quality, water sources, and soil composition. Environmental agencies and researchers utilize advanced analytical techniques to detect and quantify asbestos levels, enabling a better understanding of its ecological impact.
Efforts to manage asbestos in the natural world focus on minimizing human exposure and preserving the integrity of ecosystems, underscoring the importance of holistic approaches to asbestos testing and environmental conservation.
A Proactive Approach to Risk Mitigation
In addition to regular asbestos testing, asbestos inspections serve as a proactive and preventive measure in various environments. As explained by the professionals from GBAR Group, these inspections involve a systematic examination of buildings, infrastructure, and surrounding areas to identify potential asbestos-containing materials and assess their condition.
By conducting asbestos inspections, professionals can create a comprehensive inventory of ACMs, allowing for strategic planning and risk mitigation. The information gathered from inspections guides decisions on whether asbestos removal, encapsulation, or ongoing monitoring is the most suitable course of action.
Integrating asbestos inspections into overall safety protocols enhances the effectiveness of asbestos management programs, providing a structured and informed approach to ensure the long-term safety of individuals and the environment. The synergy between asbestos testing and inspections forms a robust framework for addressing asbestos-related risks comprehensively.
The Imperative Role of Asbestos Awareness Training
Ensuring the safety of workers in environments with potential asbestos exposure requires more than just testing and inspections—it demands comprehensive asbestos awareness training. Training programs educate employees about the risks associated with asbestos, proper safety protocols, and the correct use of personal protective equipment.
By fostering awareness, workers become more vigilant in identifying potential asbestos hazards and can contribute actively to a safer work environment. This proactive approach, coupled with regular testing and inspections, establishes a robust occupational safety culture, minimizing the risk of asbestos-related illnesses among workers.
Navigating the Complex Landscape
Navigating the complex regulatory landscape surrounding asbestos requires a deep understanding of local, national, and international guidelines. Asbestos testing and inspections play a pivotal role in ensuring regulatory compliance, as they provide the necessary data to meet stringent safety standards.
Compliance involves not only identifying and managing asbestos hazards but also documenting and reporting findings to relevant authorities. Keeping abreast of evolving regulations is crucial, as non-compliance can lead to legal ramifications and pose serious threats to public health.
A comprehensive approach that integrates asbestos testing, inspections, and regulatory compliance is essential for creating a secure and legally sound environment.
In the intricate web of asbestos management, testing, inspections, occupational safety, and regulatory compliance form the pillars of a comprehensive strategy. From industrial environments to residential buildings and natural settings, the diligent application of these measures ensures the identification, mitigation, and prevention of asbestos-related risks.
Asbestos awareness training empowers individuals, while regulatory compliance guarantees adherence to established safety standards. By weaving together these facets, we can foster a culture of safety, protect the well-being of workers and communities, and ultimately contribute to a world where the threat of asbestos is effectively managed for the benefit of all.
Table of Contents