Last updated on
As we continue to grapple with the challenges of climate change, there’s a growing urgency to find sustainable solutions for everyday necessities. One such necessity is air conditioning, which has traditionally been a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions.
However, a new era of ‘green cooling’ is upon us. This technology promises to maintain our comfort while significantly reducing our environmental impact. Let’s explore the benefits of switching to environmentally friendly air conditioning and how it could revolutionize our path towards sustainability.
Understanding Environmental Impact

Traditional air conditioning systems have long been notorious for their excessive energy consumption and the resulting carbon dioxide emissions. These units often use hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), a type of greenhouse gas that, despite being present in smaller quantities in the atmosphere than carbon dioxide, has a global warming potential thousands of times greater.
This not only contributes to global warming but also exacerbates the strain on our power grids during peak usage times, leading to brownouts and increased reliance on fossil fuel power plants.
By transitioning to green cooling technologies, we can mitigate these environmental impacts while maintaining our comfort levels. Getting air conditioning units that are energy-efficient and use eco-friendly refrigerants can significantly reduce our carbon footprint and help us move toward a more sustainable future. This, in turn, can also lead to cost savings on our energy bills and a more reliable power grid.
Energy-efficient Cooling Technologies
Energy-efficient cooling technologies are at the forefront of the green cooling revolution. One such technology is the use of geothermal heat pumps, which leverage the constant temperature of the ground to cool buildings, reducing our reliance on traditional energy sources.
Similarly, evaporative coolers, also known as “swamp coolers,” utilize the natural process of evaporation to create cooler air. This technology can be particularly effective in dry climates.
Solar air conditioning is another promising avenue. These systems harness the power of the sun, converting it into cooling energy without the need for electricity. Not only do these technologies reduce carbon emissions, but they can also lead to significant energy and cost savings in the long term, offering a win-win solution for both the environment and consumers.
Solar-powered Air Conditioning
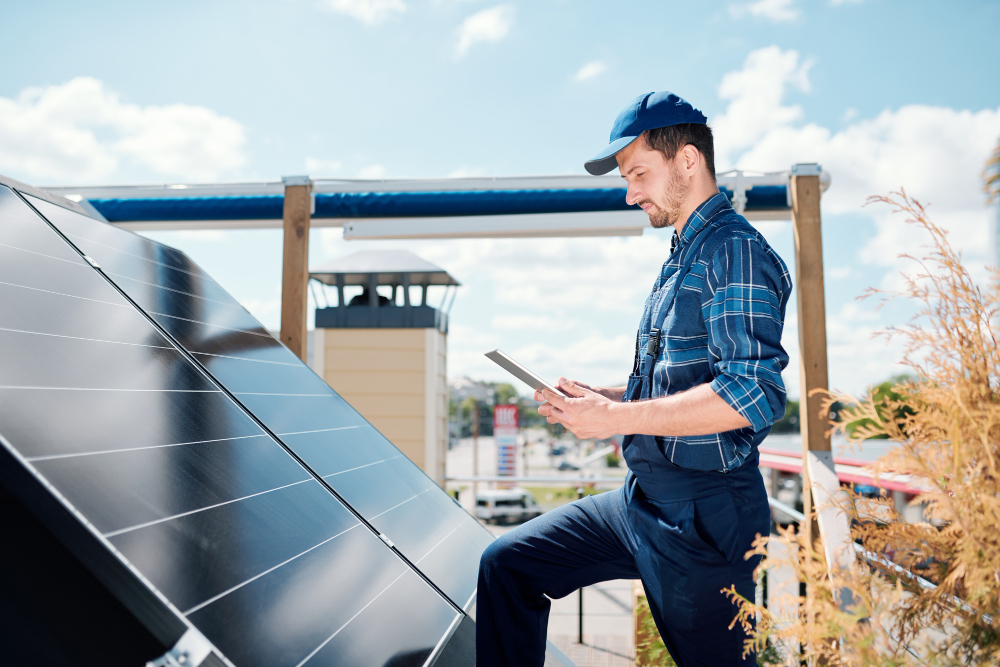

Solar-powered air conditioning represents a groundbreaking stride in renewable energy technology. By harnessing sunlight – an abundant and renewable resource – these systems convert solar energy into cool air, entirely eliminating the need for traditional electricity.
This process involves the use of solar panels, which capture sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC). This DC power then drives a DC air conditioner, providing efficient cooling without the emissions associated with conventional AC units.
Furthermore, solar air conditioning can offer significant financial savings over time. While the upfront cost can be higher than traditional systems, the reduction in energy bills and the potential for various renewable energy incentives can make it a cost-effective solution in the long run. Not to mention, the independence from the power grid reduces vulnerability to power outages and price surges.
Embracing solar-powered air conditioning can play a substantial role in our collective pursuit of a sustainable future. By reducing our reliance on fossil fuels and capitalizing on renewable energy, we can mitigate our environmental impact without compromising on our comfort.
Inverter Technology
Inverter technology is another innovation driving the shift towards green cooling. This technology, unlike traditional air conditioners that operate at a constant speed, allows the compressor in the air conditioner to vary its speed in response to the cooling demand.
When the desired temperature is reached, the inverter air conditioner doesn’t turn off; instead, it adjusts the compressor speed to maintain the temperature consistently.
By doing this, inverter technology significantly enhances energy efficiency. It leads to less power consumption, reducing energy expenses and decreasing the AC’s environmental impact.
Moreover, inverter air conditioners provide a more comfortable, stable indoor climate by eliminating the temperature fluctuations associated with traditional systems. By adopting inverter technology, we can help pave the way towards a more sustainable and comfortable future.
Eco-friendly Refrigerants
In the shift towards green cooling, the adoption of eco-friendly refrigerants is a critical component. Traditional air conditioning units often rely on Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), potent greenhouse gases that significantly contribute to global warming.
Yet, a variety of environmentally friendly alternatives are emerging. One such alternative is R32, a refrigerant with a much lower global warming potential than commonly used HFCs.
Another promising avenue is the use of natural refrigerants, such as propane, ammonia, and carbon dioxide. These substances have a significantly lower global warming potential compared to HFCs and are readily available and cost-effective.
Hydrocarbon refrigerants like R290 (propane) and R600a (isobutane) are gaining traction in residential and commercial cooling applications due to their excellent thermodynamic properties and low environmental impact.
The Takeaway
The benefits of green cooling are significant and far-reaching. By transitioning to energy-efficient technologies, harnessing solar power, adopting inverter technology, and using eco-friendly refrigerants, we can reduce our environmental impact while maintaining comfortable indoor temperatures. These solutions offer a sustainable path forward for both individuals and businesses as we work towards a greener future.
Table of Contents